Accessibility/WebAccessibilityAPI: Difference between revisions
| (47 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
readonly attribute AttributeMap attributes; | readonly attribute AttributeMap attributes; | ||
readonly attribute sequence<DOMString> patterns; | |||
readonly attribute Object toPattern(DOMString type); | readonly attribute Object toPattern(DOMString type); | ||
| Line 157: | Line 159: | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AttributeSet .''hasAnyOf'' | AttributeSet .''hasAnyOf'' | ||
::Return true if any of the | ::Return true if any of the object properties matches to the object attributes. | ||
AttributeSet .''hasAllOf'' | AttributeSet .''hasAllOf'' | ||
::Return true if all | ::Return true if all of the object properties matches to the object attributes. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
Each property of the object is a string or an array of strings. If array of strings is given then the object attribute is expected to have any of given values, empty array means the attribute value doesn't matter for match. String value and null values are treated as single element array or empty array correspondingly. | |||
<b>Example #1.</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
var attrs = { | |||
live: [ "assertive", "polite" ], | |||
relevant: "show", | |||
busy: null | |||
}; | |||
var matched = accEl.hasAllOf(attrs); | |||
// Matches if the ccessible element has "live" object attribute of | |||
// "assertive" or "polite" values, has "relevant" object attribute of | |||
// "show" value, and it has "busy" attribute. | |||
</pre> | |||
Example | <b>Example #2. Process autocomplete.</b> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var | var accEl = document.getElementById("foo").a11ement; | ||
var autocomplete = | |||
var checkObj = { autocomplete: [ "list", "both" ] }; | |||
if (accEl.attributes.hasAllOf(checkObj)) { | |||
doAutocomplete(); | |||
} | |||
// Alternatively you can do | |||
var autocomplete = accEl.attributes.get("autocomplete"); | |||
if (["list", "both"].indexOf(autocomplete) != -1) { | if (["list", "both"].indexOf(autocomplete) != -1) { | ||
doAutocomplete(); | |||
} | } | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 188: | Line 214: | ||
::Lists all notifications that qualifies for live region. | ::Lists all notifications that qualifies for live region. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
===Patterns=== | ===Patterns=== | ||
| Line 194: | Line 221: | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessibleElement .''patterns'' | |||
::Returns a list of all patterns supported by the accessible element. | |||
Object .''toPattern''(DOMString type) | Object .''toPattern''(DOMString type) | ||
::Returns an object for the pattern of given type if supported by an accessible element. | ::Returns an object for the pattern of given type if supported by an accessible element. | ||
| Line 199: | Line 229: | ||
See [[#Patters|patterns section]] for details. | See [[#Patters|patterns section]] for details. | ||
===Relations=== | ===Relations=== | ||
| Line 264: | Line 293: | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessibleElement .''actions'' | AccessibleElement .''actions'' | ||
::Returns a [[# | ::Returns a [[#ActionMap|ActionMap]] object of actions exposed by the accessible element. The returned object is not live, i.e. it is not updated if the accessible element actions change. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 345: | Line 374: | ||
====ActionMap==== | |||
==== | |||
Accessible actions are presented by <code> | Accessible actions are presented by <code>ActionMap</code> map like object of pairs { action name, action object }. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
interface | interface ActionMap { | ||
readonly maplike<DOMString, Action>; | readonly maplike<DOMString, Action>; | ||
}; | }; | ||
| Line 448: | Line 474: | ||
}); | }); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
====Questions/concerns==== | |||
* Interactions should be extended to allow to specify a control that triggers the action. The concept is described by InidieUI: you can use mouse, touchscreen, keyboard, voice control or a control element to invoke the action. Maybe Interactions should be renamed to Triggers to share terms with IndieUI. | |||
Here's the image of InideUI action/interaction concept. | |||
<div style="height: 254px; overflow: hidden;"> | |||
http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/iui-scroll.png | |||
</div> | |||
Alternatively we could introduce relations between actions like "triggers" and "triggeredby". | |||
* What about highlevel actions (uberactions), for example, "press" buttons means "send something somewhere". This may be covered by label. Another example, selected listitem on the left changes a view on the right, "select" actions has meaning of "change view". Or checkbox that enables/disables related controls, "check/uncheck" action means "enable/disable controls". These examples correlates to controlledby/controllerfor relations, but the relations doesn't reveal type of control. | |||
===Parent-child relations=== | ===Parent-child relations=== | ||
| Line 532: | Line 573: | ||
AccessiblePos? move(DOMNode container, long offset); | AccessiblePos? move(DOMNode container, long offset); | ||
AccessiblePos? move(DOMPoint); | AccessiblePos? move(DOMPoint); | ||
AccessiblePos? search(Where where, | AccessiblePos? move(Where where, Criteria); | ||
AccessiblePos? search(Where where, Criteria); | |||
readonly attribute AccessibleElement root; | readonly attribute AccessibleElement root; | ||
readonly attribute AccessibleElement? anchor; | readonly attribute AccessibleElement? anchor; | ||
readonly attribute Offset offset; | readonly attribute Offset offset; | ||
DOMRangeBound toDOM(); | |||
}; | }; | ||
| Line 549: | Line 588: | ||
====Construction==== | ====Construction==== | ||
Construction by accessible element and offset relative it. | |||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessiblePos .''Constructor''(AccessibleElement, Offset, AccessibleElement) | AccessiblePos .''Constructor''(AccessibleElement, Offset, AccessibleElement) | ||
| Line 561: | Line 603: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
The offset may be either a number, a numeric mapping of caret position in the content, or a literal. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
typedef long or OffsetLiterals Offset; | typedef long or OffsetLiterals Offset; | ||
enum OffsetLiterals { | enum OffsetLiterals { | ||
" | "before", | ||
" | "begin", | ||
"at", | "at", | ||
" | "end", | ||
" | "after" | ||
}; | }; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
OffsetLiterals .'' | OffsetLiterals .''before'' | ||
::Used to set the accessible position right before the accessible element beginning | ::Used to set the accessible position right before the accessible element beginning. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
OffsetLiterals .'' | OffsetLiterals .''begin'' | ||
::Used to set the accessible position right after the accessible element beginning | ::Used to set the accessible position right after the accessible element beginning. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
OffsetLiterals .''at'' | OffsetLiterals .''at'' | ||
::Used to set the accessible position at the accessible element | ::Used to set the accessible position at the accessible element. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
OffsetLiterals .'' | OffsetLiterals .''end'' | ||
::Used to set the accessible position right before the accessible element ending | ::Used to set the accessible position right before the accessible element ending. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
OffsetLiterals .'' | OffsetLiterals .''after'' | ||
::Used to set the accessible position right after the accessible element ending | ::Used to set the accessible position right after the accessible element ending. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
< | <b>Example #1. Input widget.</b> | ||
<pre> | |||
<input id="input" value="Hello"> | |||
<script> | |||
var input = document.getElementById("input").a11ement; | |||
// Position is at the control | |||
var p = new A11ePos(input, "at"); | |||
// Position is in the control text at 0 offset. | |||
p = new A11ePos(input, "begin"); | |||
// Position is in the control text at 5 offset. | |||
p = new A11ePos(input, "end"); | |||
</script> | |||
</pre> | |||
< | <b>Example #2. Image inside a paragraph.</b> | ||
</ | |||
<pre> | |||
<p id="p">I <img id="img" src="love.png" alt="love"> you</p> | |||
< | <script> | ||
var img = document.getElementById("img").a11ement; | |||
// The position is right before the image, at 2 offset relative the paragraph. | |||
var p = new A11ePos(img, "before"); | |||
</ | // The position is right after the image, at 3 offset relative the paragraph. | ||
p = new A11ePos(img, "after"); | |||
// The position is at the image, no offset relative the paragraph is applicable. | |||
p = new A11ePos(img, "at"); | |||
p = new A11ePos(img, "begin"); | |||
p = new A11ePos(img, "end"); | |||
</script> | |||
</pre> | |||
<b>Example #3. Table.</b> | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var | <table id="table"> | ||
<tr> | |||
<td>cell</td> | |||
</tr> | |||
</table> | |||
<script> | |||
var table = document.getElementById("table").a11ement; | |||
// The position at the table. | |||
var | var p = new A11ePos(table, "at"); | ||
var | // The position is in the table, before the row. | ||
var p = new A11ePos(table, "begin"); | |||
// The position is in the table, after the row. | |||
var p = new A11ePos(table, "end"); | |||
// The position is in the table, before the row, numeric offset is ignored. | |||
var p = new A11ePos(table, 1); | |||
</script> | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Construction from a point on the screen. See [[#Hit_testing|hit testing]] for details. | |||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessiblePos .'' | AccessiblePos .''Constructor''(DOMPoint, AccessibleElement) | ||
:: | ::Constructs the accessible position. | ||
::Parameters | ::Parameters | ||
:::'' | :::''point'' of ''DOMPoint'' | ||
::::the | ::::a point, the accessible position should be set at | ||
:::'' | :::''root'' of ''AccessibleElement'', optional | ||
:::: | ::::a root of subtree containing the position. If not provided then parent document is used. | ||
</code> | |||
Construction from a DOM node and offset relative it. See [[#Caret_and_selection|selection]] section for examples. | |||
AccessiblePos .'' | <code> | ||
:: | AccessiblePos .''Constructor''(DOMNode, long, AccessibleElement) | ||
::Constructs the accessible position from (DOMNode, offset) pair. | |||
::Parameters | ::Parameters | ||
:::''node'' of ''DOMNode'' | :::''node'' of ''DOMNode'' | ||
::::the | ::::the container node | ||
:::''offset'' of ''long'' | :::''offset'' of ''long'' | ||
::::offset | ::::offset within the container node | ||
::: | :::''root'' of ''AccessibleElement'', optional | ||
::::a root of subtree containing the position. If not provided then parent document is used. | |||
</code> | |||
Copy constructor. | |||
AccessiblePos .'' | <code> | ||
:: | AccessiblePos .''Constructor'' | ||
::Constructs the accessible position equal to given position. | |||
::Parameters | ::Parameters | ||
:::'' | :::''pos'' of ''AccessiblePos'' | ||
:::: | ::::accessible position to copy | ||
</code> | |||
====Change the position==== | |||
There is a bunch of methods to change accessible position. | |||
AccessiblePos .'' | <code> | ||
:: | AccessiblePos .''move''(AccessilbeElement, Offset) | ||
::Move the accessible position to the given anchor and offset. | |||
::Parameters | ::Parameters | ||
:::'' | :::''element'' of ''AccessibleElement'' | ||
:::: | ::::the anchor | ||
:::'' | :::''offset'' of ''Offsest'', optional | ||
:::: | ::::offset relative the anchor | ||
:::Return | :::Return itself or null if not succeeded. | ||
AccessiblePos .''move''(DOMNode, long) | |||
::Move the accessible position to the given DOM node at given offset. | |||
::Parameters | |||
:::''node'' of ''DOMNode'' | |||
::::the anchor | |||
:::''offset'' of ''long'' | |||
::::offset relative the anchor | |||
:::Return itself or null if not succeeded. | |||
AccessiblePos .''move''(DOMPoint) | |||
:: | ::Move the accessible position in the content. Returns true if succeeded. | ||
::Parameters | |||
:::''point'' of ''DOMPoint'' | |||
::::the point the accessible position should be moved to. | |||
:::Return itself or null if not succeeded. | |||
====Move through the content==== | |||
Accessible position can be moved through the content by criteria. | |||
Where .'' | AccessiblePos .''move'' (''Where'', ''Criteria'') | ||
:: | ::Move the accessible position to the content complying with criteria. | ||
::Parameters | |||
:::''where'' of ''Where'' | |||
::::where the search should be performed | |||
:::''criteria'' of ''Criteria'' | |||
::::function describing a match | |||
:::Return itself if succeeded, otherwise null. | |||
Where | AccessiblePos .''search'' (''Where'', ''Criteria'') | ||
::Search for a match | ::Search for content of the given criteria relative the accessible position. | ||
::Parameters | |||
:::''where'' of ''Where'' | |||
::::where the search should be performed | |||
:::''criteria'' of ''Criteria'' | |||
::::function describing a match | |||
:::Return new instance if succeeded, otherwise null. | |||
</code> | |||
Where | =====Where to search===== | ||
Where . | The search area and the way accessible elements are traversed are defined by <code>Where</code> argument. It defines whether traversal is perfromed by accessible tree hierarchy or by layout on the screen, and whether the traversal is relative of the current position or relative of the root. | ||
Where | <pre> | ||
enum Where { | |||
"forward", | |||
"backward", | |||
"cyclic forward", | |||
"cyclic backward", | |||
"tofirst", | |||
"tolast", | |||
"left", | |||
"right", | |||
</ | "up", | ||
"down", | |||
"above", | |||
"under", | |||
"closest" | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
<code> | |||
Where .''forward'' | |||
::Search after the accessible position. | |||
Where .''backward'' | |||
::Search backwards from the accessible position. | |||
Where .''cyclic forward'' | |||
::Search forwards from the accessible position in cycle. | |||
Where .''cyclic backward'' | |||
::Search backwards from the accessible position in cycle. | |||
Where .''first'' | |||
::Search for a first match inside the root. | |||
Where .''last'' | |||
::Search backwards (from last to first element) for a first match inside the root. | |||
Where .''left'' | |||
::Search for a match left to the position. | |||
Where .''right'' | |||
::Search for a match right to the position. | |||
Where .''up'' | |||
::Search for a match up from the position. | |||
Where .''down'' | |||
::Search for a match down from the position. | |||
:: | |||
Where .''above'' | |||
::Search for a match above the position. | |||
Where .''under'' | |||
::Search for a match under the position. | |||
Where .''closest'' | |||
::Search for a geometrically closest match to the position. | |||
</code> | |||
<b>Example.</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
function criteria(el) { } | |||
var pos1 = new A11ePos(new DOMPoint(x, y), a11edoc).move("forward", criteria); | |||
var pos2 = new A11ePos(elm, "at").move("backward", criteria); | |||
var pos3 = new A11ePos(pos).move("forward", criteria); | |||
or | |||
var pos2 = pos2.search("forward", criteria); | |||
</pre> | |||
=====Criteria===== | |||
Criteria can be either a literal describing how the position should be moved or a matching function called for every traversed accessible. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
enum | typedef CriteriaLiteral or CriteriaFunc Criteria; | ||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
enum CriteriaLiteral { | |||
"char", | "char", | ||
"word", | "word", | ||
| Line 791: | Line 902: | ||
"paragraph", | "paragraph", | ||
"change", | "change", | ||
"bit | "bit" | ||
}; | }; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''char'' | |||
::Used to move the position one char long. | ::Used to move the position one char long. | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''word'' | |||
::Used to move the position to the next word. | ::Used to move the position to the next word. | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''sentence'' | |||
::Used to move the position to the next sentence. | ::Used to move the position to the next sentence. | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''line'' | |||
::Used to move the position to beginning of next line or end of previous line. | ::Used to move the position to beginning of next line or end of previous line. | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''paragraph'' | |||
::Used to move the position to beginning of next/previous paragraph. | ::Used to move the position to beginning of next/previous paragraph. | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''change'' | |||
::Used to move the position to next change either of text attribute or new accessible. | ::Used to move the position to next change either of text attribute or new accessible. | ||
CriteriaLiteral .''bit'' | |||
::Used to move the position to next/previous navigable position. For example, from accessible start inside of it to right before accessible outside of it or moving from end of this line to start of next line in case of soft line break lines. | ::Used to move the position to next/previous navigable position. For example, from accessible start inside of it to right before accessible outside of it or moving from end of this line to start of next line in case of soft line break lines. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
< | <b>Example #1. Traverse a paragraph by words.</b> | ||
<pre> | |||
var p = document.getElementById("p").a11ement; | |||
var pos1 = new A11ePos(p, "begin", p), pos2 = null; | |||
while (pos2 = pos1.search("forward", "word")) { | |||
console.log(pos2.text(pos1)); | |||
pos1 = pos2; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
<p id="p">Mozilla is a <a href="">free-software</a> community which | |||
produces the <a href="">Firefox web browser</a>.</p> | |||
</pre> | |||
The script above generates the log "Mozilla ", "is ", "a ", "free-", "software ", "community", "which ", "produces ", "the ", "Firefox ", "web ", "browser." | |||
<pre> | |||
<p id="p">Mo<a href="">zilla</a>.</p> | |||
</ | </pre> | ||
The log is "Mozilla". | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
callback CriteriaFunc = CriteriaLiteral or Offset or "next" (AccessibleElement); | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
< | <code> | ||
CriteriaFunc | |||
</ | ::A criteria function used to define an algorithm of the match. | ||
::Returns | |||
:::a criteria term or offset(s) | |||
</code> | |||
If "next" is returned then criteria function is reentered with next traversed accessible. If offset is given then traversing is stopped, the accessible position is moved to the traversed accessible element and given offset. If criteria literal is returned then the accessible position is moved to the position complying the criteria. If it cannot be moved withing current accessible then it reenters with next accessible. | |||
<b> Example. Navigate by widgets and structures, and by words in case of text.</b> | <b> Example. Navigate by widgets and structures, and by words in case of text.</b> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
function | function criteria(aEl) | ||
{ | { | ||
var role = document.taxonOf("role", | var role = document.taxonOf("role", aEl.role); | ||
if (role.is("widget") | if (role.is("widget") | ||
return | return "at"; | ||
if (role.is("structure") | if (role.is("structure") | ||
return "at"; | return "at"; | ||
// Reenters with next accessible if it cannot move to the next | // Reenters with next accessible if it cannot move to the next line within this accessible. | ||
if (role.is("textcontainer")) | if (role.is("textcontainer")) | ||
return " | return "line"; | ||
return "next"; | return "next"; | ||
} | } | ||
pos.move("next", | pos.move("next", criteria); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
====Other methods==== | ====Other methods==== | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessiblePos .''root'' | |||
::Returns the accessible element the position movement is restricted to. | |||
AccessiblePos .''anchor'' | AccessiblePos .''anchor'' | ||
::Returns the accessible element the position is contained by. | ::Returns the accessible element the position is at or contained by. | ||
AccessiblePos .''offset'' | |||
AccessiblePos .'' | ::Return an offset of the accessible position, either numeric or text. | ||
:: | |||
AccessiblePos .''toDOM'' | |||
::Returns DOMRangeBound object which is a pair of DOM node and content offset relative it. | |||
</code> | </code> | ||
<pre> | |||
dictionary DOMRangeBound { | |||
DOMNode node; | |||
long offset; | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
===Virtual cursor=== | ===Virtual cursor=== | ||
| Line 923: | Line 1,026: | ||
Whenever the virtual cursor position is changed then ''cursor_moved'' event is fired. | Whenever the virtual cursor position is changed then ''cursor_moved'' event is fired. | ||
Questions/concerns | ===Questions/concerns=== | ||
* Do we need *is* method right on AccessibleElement or should we have Role interface having that method or should AccessibleElement return role taxa as a role. | |||
* Do we need to have "inContextOf" on AccessibleElement to check what the accessilbe belongs to. Note, native implementation doing some cache may be faster than tree traversal. If we need it then it's worth to consider *is* method too. | |||
* Do we need isAnyOf() method additionally? | |||
* Do we need to compare() method to compare two positions | |||
* Ensure that the virtual cursor is survivable. If it ends up in the hidden sub-tree for example. If subtee gets destroyed then cursor should be moved. If AccessiblePos doesn't have matching function then it's unclear where it should be moved. | * Ensure that the virtual cursor is survivable. If it ends up in the hidden sub-tree for example. If subtee gets destroyed then cursor should be moved. If AccessiblePos doesn't have matching function then it's unclear where it should be moved. | ||
* Also take into account walking to/from parent/child frames | * Also take into account walking to/from parent/child frames | ||
* Should it be outlined as moved? | |||
* Yura: we should have async API for search. | |||
[ Promise variant if we had async API]. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
partial interface AccessiblePos { | function getText() { | ||
DOMString | var p = new A11ePos().move("first", a => a.role == "paragraph"); | ||
readonly attribute AttributeSet textAttributes; | var startPos; | ||
}; | return p.then(function(pos) { | ||
</pre> | startPos = pos; | ||
return pos.search("forward", a => "line"); }). | |||
then(function(endPos) { | |||
return startPos.textInBetween(endPos); | |||
}; | |||
} | |||
getText().then(function(text) { /* Say text */ }) | |||
</pre> | |||
==Text== | |||
<pre> | |||
partial interface AccessiblePos { | |||
DOMString text(AccessiblePos pos); | |||
DOMString text(CriteriaLiteral criteria); | |||
readonly attribute AttributeSet textAttributes; | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessibleDocument .'' | AccessibleDocument .''text(AccessiblePos)'' | ||
::Returns the text enclosed between this and given accessible positions. | ::Returns the text enclosed between this and given accessible positions. | ||
AccessibleDocument .''text(CriteriaLiteral)'' | |||
::Returns the text at the position complying the given criteria. See [[#Criteria|criteria]] for options. | |||
</code> | </code> | ||
Example how to get first line of the first encountered paragraph: | Example how to get first line of the first encountered paragraph: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var startPos = new A11ePos().move("first", | function criteria(a) | ||
var endPos = startPos && startPos.search("forward", | { return a.role == "paragraph" ? "being" : "next" }; | ||
var text = startPos. | var startPos = new A11ePos(document).move("first", criteria); | ||
var endPos = startPos && startPos.search("forward", "line"); | |||
var text = startPos.text(startPos, endPos); | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
or same effect by using criteria literal | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
function | function criteria(a) | ||
{ return a.role == "paragraph" ? "being" : "next" }; | |||
var pos = new A11ePos(document).move("first", criteria); | |||
var text = pos.text("line"); | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 994: | Line 1,118: | ||
p.textAttributes.get("font-weight") == 700; // true | p.textAttributes.get("font-weight") == 700; // true | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==Caret and selection== | ==Caret and selection== | ||
| Line 1,017: | Line 1,140: | ||
AccessibleDocument .''selectionStart'' | AccessibleDocument .''selectionStart'' | ||
::Get/set selection start. | ::Get/set selection start. | ||
AccessibleDocument .''selectionEnd'' | AccessibleDocument .''selectionEnd'' | ||
| Line 1,024: | Line 1,146: | ||
<b>Example</b> | <b>Example.</b> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 1,031: | Line 1,153: | ||
var pos2 = new A11ePos(pos.anchor.nextSibling); | var pos2 = new A11ePos(pos.anchor.nextSibling); | ||
document.a11ement.selectionEnd = pos; | document.a11ement.selectionEnd = pos; | ||
</pre> | |||
<b>Example #2. Connection with DOM selection.</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
var sel = window.getSelection(); | |||
var pos1 = new A11ePos(sel.anchorNode, sel.anchorOffset); | |||
var pos2 = new A11ePos(sel.focusNode, sel.focusOffset); | |||
var p1 = pos1.toDOM(); | |||
sel.getRangeAt(0).setStart(p1.node, p1.offset); | |||
var p2 = pos2.toDOM(); | |||
sel.getRangeAt(0).setEnd(p2.node, p2.offset); | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
==Geometry== | ==Geometry== | ||
Outline can | The section contains bunch of methods and approaches to deal with web page geometry. | ||
===Outline=== | |||
AT can outline a position or a range enclosed between two positions. This feature is useful to track stuff like virtual cursor. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
partial interface AccessibleDocument { | partial interface AccessibleDocument { | ||
void outline(AccessiblePos pos1, AccessiblePos pos2); | void outline(AccessiblePos pos1, optional AccessiblePos pos2); | ||
void clearOutlines(); | void clearOutlines(); | ||
}; | }; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessibleDocument .''outline'' | AccessibleDocument .''outline'' | ||
::Outlines a range | ::Outlines a position if second position is omitted. If second position is omitted then outlines a collapsed range. | ||
AccessibleDocument .''clearOutlines'' | AccessibleDocument .''clearOutlines'' | ||
| Line 1,052: | Line 1,190: | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
===Geometrical navigation=== | |||
AT can scan the web page by moving the position geometrically up/down/left/right. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var scanner | |||
{ | |||
start: function() { | |||
if (this.stopped) | |||
return; | |||
var nextpos = this.pos.move("right", this.controller); | |||
if (!nextpos) | |||
nextpos = this.pos.move("down", this.controller); | |||
if (nextpos) { | |||
document.outline(nextpos); | |||
: | window.setTimeout(this.start.bing(this), 1000); | ||
} | |||
}, | |||
stop: function() { | |||
this.stopped = true; | |||
}, | |||
controller: function(aEl) { | |||
var role = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", aElm.role); | |||
if (role.is("widget")) | |||
return "at"; | |||
return "next"; | |||
} | |||
pos: new A11ePos(new DOMPoint(0, 0)), | |||
stopped: false | |||
} | |||
</pre> | |||
===Hit testing=== | ===Hit testing=== | ||
| Line 1,096: | Line 1,247: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Questions/concerns | |||
*Outline: it's tricky to style that but maybe document or accessible should decide how it should be styled, for example, black outline on black background. | |||
*Do we need a way to return coordinates of accessible position's edge points? | |||
*Do we need a method to calculate distance between two positions? | |||
*Do we need a method to calculate boundaries (aka containing rect)? | |||
*Do we need a method to check whether the given point is contained by a range? | |||
==Events== | ==Events== | ||
| Line 1,250: | Line 1,401: | ||
<div id="JSSource"> | ==Multiprocessing== | ||
Accessible tree is scoped to a process, i.e. you can have seamless accessible tree between all document frames until it violates security policy. In case of multiprcess frames you have to use standard mechanism to communicate between processes. | |||
When the virtual cursor reaches a frame start or end and it was attempted to move it further then message is sent to a process where the virtual cursor would go in case of single process. | |||
Questions/concerns | |||
* what messaging mechanism should be used | |||
* should it be allowed to move from iframe to parent document? | |||
<div id="JSSource"> | |||
==Make the content accessible== | ==Make the content accessible== | ||
| Line 1,344: | Line 1,506: | ||
control.relations.add("labelledby", label.a11yment); | control.relations.add("labelledby", label.a11yment); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 1,382: | Line 1,541: | ||
readonly attribute object attributes; | readonly attribute object attributes; | ||
readonly attribute object relations; | readonly attribute object relations; | ||
readonly attribute sequence<DOMString> patterns; | |||
object toPattern(DOMString); | |||
readonly attribute DOMString text; | readonly attribute DOMString text; | ||
object textAttributesAt( | object textAttributesAt(Offset); | ||
readonly attribute object actions; | readonly attribute object actions; | ||
| Line 1,502: | Line 1,664: | ||
In this case the <code>labelledby</code> relation getter is more powerful than its ARIA version and all computations are running iff somebody inquired the relation. | In this case the <code>labelledby</code> relation getter is more powerful than its ARIA version and all computations are running iff somebody inquired the relation. | ||
====Patterns==== | |||
<code> | |||
AccessibleSource .''patterns'' | |||
::Returns a list of all patterns implemented by the accessible element. | |||
</code> | |||
<code> | |||
AccessibleSource .''toPattern'' | |||
::Returns an object for the given pattern. If the method is not provided then the source object has to implemented itself all claimed patterns. | |||
</code> | |||
<b>Example #4. Implement patterns.</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
var slider = { | |||
role: "slider", | |||
patterns: [ "value" ], | |||
toPattern: function(aName) { | |||
return aName == "value" ? this : null; | |||
}, | |||
min: 0, | |||
max: 100, | |||
value: 0 | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
====Text==== | ====Text==== | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessibleSource .''text'' | |||
::Return the text. | ::Return the text. | ||
AccessibleSource .''textAttributesAt'' | |||
::Returns object of { name: value } pairs representing text attributes at given offset within the accessible element text. | ::Returns object of { name: value } pairs representing text attributes at given offset within the accessible element text. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<b> Example # | <b> Example #5. Text content.</b> | ||
While text should be normally in the content, there are cases when the author has to provide it for non-text content. For example, this technique can be used to turn HTML image into text. | While text should be normally in the content, there are cases when the author has to provide it for non-text content. For example, this technique can be used to turn HTML image into text. | ||
| Line 1,552: | Line 1,745: | ||
<b>Example # | <b>Example #6. Describe actions and interactions.</b> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 1,571: | Line 1,764: | ||
In case if interactions cannot be provided then the accessible source have to implement <code>activate</code> method to invoke actions. | In case if interactions cannot be provided then the accessible source have to implement <code>activate</code> method to invoke actions. | ||
==== | ====Inheritance==== | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
AccessibleSource .'' | AccessibleSource .''element'' | ||
:: | ::Refers to the accessible element implementation as there were no accessible source attached to it. Set by the browser when the accessible source is attached to the accessible element. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<b>Example. Lazy extension of accessible relations.</b> | |||
The web developer can alter existing accessible tree including subtree creations and deletions. This can be done either by <code>AccessibleSource</code> object assigned to the accessible element or by direct manipulations on the accessible tree. | <pre> | ||
var source = { | |||
get relations() { | |||
var r = this.element.relations; | |||
r.add("labelledby", document.querySelector(this.selector)); | |||
return r; | |||
}, | |||
element: null, | |||
selector: "" | |||
}; | |||
document.getElementById("button").accessibleSource = source; | |||
</pre> | |||
===Change the accessible tree=== | |||
The web developer can alter existing accessible tree including subtree creations and deletions. This can be done either by <code>AccessibleSource</code> object assigned to the accessible element or by direct manipulations on the accessible tree. | |||
====Direct tree alteration==== | ====Direct tree alteration==== | ||
| Line 1,693: | Line 1,901: | ||
onactivated: function(aEvent) { | onactivated: function(aEvent) { | ||
if (aEvent.region == "button") | if (aEvent.region == "button") | ||
this. | this.element.set("focused"); | ||
else | else | ||
this. | this.element.states.unset("focused"); | ||
} | } | ||
element: null // set by the browser | |||
}; | }; | ||
| Line 1,706: | Line 1,914: | ||
===Feedback notifications=== | ===Feedback notifications=== | ||
Accessible element may be notified of any kind of event, including about property change when managed by connected source object. When notified the browser may fire accessible events and update its cache if necessary. Decision whether to notify the browser or not should be based on the accessible events model. In other words if a property change in native markup causes accessible event then it's quite likely the event is expected for similar accessible source change. | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 1,719: | Line 1,927: | ||
::Called when source has been changed to notify the host accessible element about property change. The browser is responsible to fire proper accessible events and update its internal representation. | ::Called when source has been changed to notify the host accessible element about property change. The browser is responsible to fire proper accessible events and update its internal representation. | ||
::Parameters | ::Parameters | ||
::: | :::eventType of DOMString | ||
:::: | ::::The event type to fire. | ||
::: | :::attrs | ||
:::: | ::::Attributes describing the event. See [[#Event_types|event types]] for attributes variety. | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| Line 1,741: | Line 1,949: | ||
} | } | ||
}; | }; | ||
function onfocus(aEvent) { | |||
// Change accessible properties when element is focused. | |||
// The change requires accessible events. | |||
aEvent.target.accessibleSource = listboxSource; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Implied semantics=== | ===Implied semantics=== | ||
The author | The idea is to help the author to keep the code less verbose as possible. If role implies a number of preset attributes or states then they are present on the accessible element by default, i.e. if the author didn't list them. For example, if <code>listitem</code> role is selectable and focusable by default then the author doesn't have to point <code>selectable</code> and <code>focusable</code> states when he describes a listitem source, in other words, these code snippets are equivalent: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var | var source1 = { | ||
role: "listitem" | role: "listitem" | ||
}; | }; | ||
var source2 = { | |||
var | |||
role: "listitem", | role: "listitem", | ||
states: [ "selectable" ] | states: [ "selectable", "focusable" ] | ||
}; | }; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Implied semantics is described by [[#SemanticsProviders|taxonomies]]. | |||
===Conflicts=== | ===Conflicts=== | ||
[to be done conflicts between native semantics, ARIA and this API] | [to be done conflicts between native semantics, ARIA and this API, I tend to think that the author should be able to replace/remove native semantics if needed. This can ruin the web page but it gives the absolute control over the page content. A dangerous but quite powerful tool like atomic energy. ] | ||
===Sniffing=== | ===Sniffing=== | ||
In order to make optimization the content provider has to know whether accessibility consumer is active. The provider can add a callback for <code>deploy</code> and <code>conceal</code> event types which will be triggered when consumer appears/gets inactive. | In order to make an optimization, the content provider has to know whether an accessibility consumer (like screen reader) is active. The provider can add a callback for <code>deploy</code> and <code>conceal</code> event types which will be triggered when consumer appears/gets inactive. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 1,926: | Line 2,139: | ||
} | } | ||
}; | }; | ||
document. | document.a11ement.import("role", taxa); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var taxon = document. | var taxon = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", "checklistitem"); | ||
if (taxon.is("menuitem")) { | if (taxon.is("menuitem")) { | ||
// process menuitem selection | // process menuitem selection | ||
| Line 1,939: | Line 2,152: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var taxon = document. | var taxon = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", "main"); | ||
var isLandmark = taxon.attributes.has("landmark"); | var isLandmark = taxon.attributes.has("landmark"); | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 1,946: | Line 2,159: | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var taxon = document. | var taxon = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", "listbox"); | ||
print(listboxRole.relations.get("states"))); // prints "focusable" | print(listboxRole.relations.get("states"))); // prints "focusable" | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 1,996: | Line 2,209: | ||
<div id="TaxonomyTypes"> | <div id="TaxonomyTypes"> | ||
===Taxonomy types=== | ===Taxonomy types=== | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Each taxonomy is described means of its own interface which is used to define the hierarchy and interconnections between taxonomies. If taxon refers to taxa of other taxonomy type then a string describing the reference may be in form of "taxon:modifier", where taxon is a name of related taxon and modifier is an extra information about how the taxa are interconnected. For example, role taxon may be connected to "live" taxon of attributes taxonomy by placing "live:assertive" value in <code>attributes</code> field which means that the role supports "live" object attribute and its default value is "assertive" on it. | |||
====Roles==== | ====Roles==== | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
dictionary | dictionary RoleTaxon { | ||
DOMString landmark; | DOMString landmark; | ||
DOMString description; | DOMString description; | ||
sequence<DOMString> parents; | |||
sequence<DOMString> owns; | |||
sequence<DOMString> states; | |||
Object attributes; | Object attributes; | ||
sequence<DOMString> relations; | |||
sequence<DOMString> actions; | |||
}; | }; | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 2,015: | Line 2,233: | ||
<code> | <code> | ||
RoleTaxon .''landmark'' | |||
::Navigation landmark name if applicable. | ::Navigation landmark name if applicable. | ||
RoleTaxon .''description'' | |||
::Localized role description. | ::Localized role description. | ||
RoleTaxon .''parents'' | |||
::List of roles the role is inherited from. | ::List of roles the role is inherited from. | ||
RoleTaxon .''owns'' | |||
::List of roles allowed in children of the role. Used for validation. | ::List of roles allowed in children of the role. Used for validation. | ||
RoleTaxon .''states'' | |||
::List of states allowed on the role. | ::List of states allowed on the role. Optional modifier is "default" which points out that the state is exposed on the role until explicitly specified otherwise. See [[#Implied_semantics|implied semantics]]. | ||
RoleTaxon .''attributes'' | |||
::List of attributes supported by the role. Default value of the attribute may be specified as modifier. For example, "live:polite" points out that "live" object attribute has "polite" value by default. If default value is not specified then it's taken from referred attribute taxon description. | |||
RoleTaxon .''relations'' | |||
::List of relations supported by the role. | |||
RoleTaxon ..''actions'' | |||
::List of | ::List of supported actions. Actions from the list are exposed on the accessible element depending on states present on it. For example, if supported actions are "check" and "uncheck", then "check" is exposed if the accessible element doesn't have "checked" state, otherwise "unchecked". | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
<b>Example. ARIA <code>textbox</code> role.</b> | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
var taxa = { | |||
} | widget: { } | ||
input: { | |||
parents: [ "widget" ], | |||
states: [ "focusable:default", "focused" ] | |||
}, | |||
textbox: { | |||
description: "text field", | |||
parents: [ "input" ], | |||
states: [ | |||
"singleline:default", "multiline", | |||
"editable", "readonly", | |||
"required" | |||
], | |||
attributes: [ "autocomplete" ] | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
<b>Example. ARIA <code>checkbox</code> role.</b> | |||
= | <pre> | ||
var taxa = { | |||
checkbox: { | |||
description: "checkbox", | |||
parents: [ "input" ], | |||
states: [ "checkable:default, "checked" ], | |||
actions: [ "check", "uncheck" ] | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
<b>Example. ARIA <code>log</code> role.</b> | |||
= | <pre> | ||
var taxa = { | |||
region: { | |||
}, | |||
log: { | |||
parents: [ "region" ], | |||
attributes: [ "live:polite" ] | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
====States==== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
dictionary StateTaxon { | |||
DOMString description; | |||
sequence<DOMString> dependents; | |||
DOMString exclusives; | |||
} | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
< | <code> | ||
StateTaxon .''description'' | |||
::Localized taxa description. | |||
StateTaxon .''dependents'' | |||
::List of all dependent states. For example, "focused" state always accompanied by "focusable" state. | |||
StateTaxon ..''exclusives'' | |||
::Mutually exclusive states if applicable. For example, if "vertical" state is applied then "horizontal" is not and vice versa. | |||
</code> | |||
<b>Example.</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
var taxa = { | |||
focusable: { | |||
dependents: [ "focused" ] | |||
}, | |||
focused: { }, | |||
singleline: { | |||
exlcusives: [ "multiline" ] | |||
}, | |||
multiline: { | |||
exlcusives: [ "singleline" ] | |||
}, | |||
readonly: { }, | |||
editable: { }, | |||
required: { }, | |||
checked: { | |||
exlusives: [ "mixed" ] | |||
}, | |||
mixed: { | |||
exlusives: [ "checked" ] | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
====Attributes==== | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
role 'note' relations: | interface AttributeTaxon { | ||
crescendo: [note, ...] a list a notes the crescendo is applied to | DOMString description; | ||
sequence<DOMString> values; | |||
DOMString default; | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
<code> | |||
AttributeTaxon .''description'' | |||
::Localized description of the taxon | |||
AttributeTaxon .''values'' | |||
::List of all possible values of the attrbiute | |||
AttributeTaxon .''default'' | |||
::Default attribute value. Takes a place if role taxa pointing to it doesn't have own default value of it. | |||
</code> | |||
<b>Example</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
var taxa = { | |||
autocomplete: { | |||
values: [ "none", "list", "inline", "both" ], | |||
default: "none" | |||
}, | |||
live: { | |||
values: [ "none", "polite", "assertive" ], | |||
default: "none" | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
====Actions==== | |||
<pre> | |||
dictionary ActionTaxon { | |||
DOMString description; | |||
DOMString dual; | |||
sequence<DOMString> states; | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
<code> | |||
ActionTaxon .''description'' | |||
::Localized action description. | |||
ActionTaxon .''dual'' | |||
::Dual action taxon. When action is invoked, it is switched to its dual action if applicable. | |||
ActionTaxon .''states'' | |||
::Implied states. When action is invoked, states of dual action are cleared, this action states are set. | |||
</code> | |||
<b>Example.</b> | |||
<pre> | |||
var taxa = { | |||
check: { | |||
description: "check", | |||
dual: "uncheck", | |||
states: [ "checked" ] | |||
}, | |||
uncheck: { | |||
description: "uncheck", | |||
dual: "check" | |||
} | |||
}; | |||
</pre> | |||
=HTML and beyond= | |||
This doc introduces common patterns to express the semantics of markup languages to accessibility. Markup specifics is not a target for this doc in general. Each markup specification has to take care to describe their accessibility stuff in terms of this API. | |||
=Extensibility= | |||
The web application might need to extend default taxonomies to express the new semantics. For example, the web service publishing music sheets can introduce new characteristics like role, states, etc to describe music sheet content. However the web application should take care to explain new characteristic by extending default taxonomies, i.e. by describing the connection between old and new characteristics. That will resolve any backward compatibility issue, so if the consumer doesn't know about new roles then he can still figure out a closest match it's aware about. For example, if the web app author introduces "x-redbutton' and provides a role taxonomy for it saying this is an extension of 'button' role, then the consumer unfamiliar with 'x-redbutton' role will treat it as a button. | |||
The author should follow name convention to avoid potential collisions with future additions into the spec predefined lists. Thus all names should be prefixed by 'x-' like 'x-redbutton' from example above. | |||
==Music sheet example== | |||
To make a music sheet accessible the web app may introduce bunch of new roles, attributes and relations: | |||
<pre> | |||
roles: | |||
'sheet' - inherited from 'section' | |||
'note' - inherited from 'image', describes the note | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
role 'sheet' attributes: | |||
instrument: DOMString, | |||
tempo: number/DOMString | |||
clef: DOMString | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
role 'note' attributes: | |||
key: enum { C, D, E, F, G, A, H }, | |||
alteration: enum { none, flat, sharp }, | |||
octave: enum { ... }, | |||
duration: number, | |||
effects: sequence<DOMString>, // tremolo, bend | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
role 'note' relations: | |||
crescendo: [note, ...] a list a notes the crescendo is applied to | |||
diminuendo: [note, ...] a list a notes the diminuendo is applied to | diminuendo: [note, ...] a list a notes the diminuendo is applied to | ||
</pre> | |||
Or in terms of taxonomies: | |||
<pre> | |||
document.import("role", { | |||
sheet: { | |||
description: "sheet", | |||
attributes: [ "instrument", "tempo", "clef" ] | |||
}, | |||
note: { | |||
description: "note", | |||
attributes: [ "key", "alteration", "octave", "duration", "effects" ], | |||
relations: [ "crescendo", "diminuendo" ] | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
document.import("attributes", { | |||
instrument: { | |||
description: "instrument type" | |||
}, | |||
tempo: { | |||
description: "tempo" | |||
}, | |||
clef: { | |||
description: "clef" | |||
}, | |||
key: { | |||
description: "key", | |||
values: [ "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "A", "H" ], | |||
}, | |||
alteration: { | |||
description: "alteration", | |||
values: [ "none", "flat", "sharp" ], | |||
default: "none" | |||
}, | |||
octave: { | |||
description: "octave", | |||
values: [ "contra", "great", "small", "1line", "2line" ], | |||
}, | |||
duration: { | |||
description: "duration" | |||
}, | |||
effects: { | |||
description: "effects" | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
document.import("relations", { | |||
crescendo: { | |||
description: "crescendo" | |||
}, | |||
diminuendo: { | |||
description: "diminuendo" | |||
} | |||
}); | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:06, 8 May 2015
Introduction
There's number of objectives on the web to improve accessibility and usability support. Web applications want to provide special support for their users, helping them navigate and perceive the content. The browser has a number of add-ons serving to improve accessibility support, for example, the app letting to navigate landmarks on the web page. These tasks require accessibility API similar to what desktop assistive technologies have.
Web accessibility API also allows for in-browser automated accessibility testing of web content, i.e. helpful for checking that HTML and other standards in the browser are accessible to all users.
On the other hand there's a growing need for making graphical content accessible. These are charts, graphs and other various visual forms that are drawn using HTML canvas or SVG. There's also a tendency to use HTML canvas element in place of DOM because of performance matter, here's an example. All markup in the example is defined in JavaScript and there is a need for a non-DOM accessibility solution to make the content accessible.
Web accessibility API
The API provides bunch of interfaces that are used to express the web content the way the assistive technologies (AT) knows how to deal with. In other words each piece of semantically meaningful content has associated accessible element the AT operates at. The interfaces allow to receive accessible element properties, traverse the hierarchy and interact with content.
Also the API provides a way to extend existing semantics of the markup and add new semantics for inaccessible content like canvas drawings.
Accessible element
This is a basic interface providing an access to the accessible element.
interface AccessibleElement {
attribute DOMString role;
attribute DOMString name;
attribute DOMString description;
attribute DOMString value;
readonly attribute StateSet states;
readonly attribute AttributeMap attributes;
readonly attribute sequence<DOMString> patterns;
readonly attribute Object toPattern(DOMString type);
readonly attribute RelationMap relations;
AccessibleElement? relativeOf(DOMString type);
readonly attribute ActionMap actions;
void activate(DOMString action);
readonly attribute InteractionMap intreactions;
readonly attribute AccesibleElement? parent;
readonly attribute AccesibleElement? firstChild;
readonly attribute AccesibleElement? lastChild;
readonly attribute AccesibleElement? nextSibling;
readonly attribute AccesibleElement? previousSibling;
readonly attribute AccessibleChildren children;
readony attribute Node? DOMNode;
attribute AccessibleSource? source;
};
Node interface extension
Accessible element can be requested from a DOM node if the DOM node is accessible, i.e. it expresses meaningful semantics to the assistive technology.
partial interface Node {
AccessibleElement? accessibleElement;
A11eElement? a11ement; // nicer and shorter verison? // another version: accElement, accEl
};
Role
AccessibleElement .role
- Returns accessible role as a string. Examples: "button", "menu", "textfield".
Text properties
AccessibleElement .name
- Returns accessible name.
AccessibleElement .description
- Returns accessible description.
AccessibleElement .value
- Returns accessible value if applicable.
States
AccessibleElement .states
- Returns a StateSet live object for all accessible states of an accessible element.
Accessible states of an accessible element are presented by the StateSet object. It is a live object, i.e. if the states of the accessible element change then the object reflects that. Implementation is not required to compute any state until requested.
interface StateSet {
readonly setlike<DOMString>;
boolean hasAnyOf(DOMString ... states);
boolean hasAllOf(DOMString ... states);
};
StateSet .hasAnyOf
- Returns true if any of the given states are present on the accessible element.
StateSet .hasAllOf
- Returns true if all given states are present on the accessible element.
Example of a script that logs to console all accessible element states.
var accEl = document.getElementById("foo").accessibleElement;
for (let state of accElm.states) {
console.log(state);
}
Attributes
The accessible element may support a number of attributes to express the semantics that cannot be described by base properties of an accessible element.
AccessibleElement .attributes
- Returns a AttributeMap live object for all object attributes exposed on the accessible element. If accessible element attributes are changed then the object reflects the actual state of attributes. The implementation is not required to pre-compute any of the attributes.
AttributeMap
AttributeMap is an interface aimed to work with {name, value} pairs of accessible attributes.
interface AttributeMap {
readonly maplike<DOMString, any>;
boolean hasAnyOf(Object map); // Needs more work
boolean hasAllOf(Object map); // Needs more work
};
AttributeSet .hasAnyOf
- Return true if any of the object properties matches to the object attributes.
AttributeSet .hasAllOf
- Return true if all of the object properties matches to the object attributes.
Each property of the object is a string or an array of strings. If array of strings is given then the object attribute is expected to have any of given values, empty array means the attribute value doesn't matter for match. String value and null values are treated as single element array or empty array correspondingly.
Example #1.
var attrs = {
live: [ "assertive", "polite" ],
relevant: "show",
busy: null
};
var matched = accEl.hasAllOf(attrs);
// Matches if the ccessible element has "live" object attribute of
// "assertive" or "polite" values, has "relevant" object attribute of
// "show" value, and it has "busy" attribute.
Example #2. Process autocomplete.
var accEl = document.getElementById("foo").a11ement;
var checkObj = { autocomplete: [ "list", "both" ] };
if (accEl.attributes.hasAllOf(checkObj)) {
doAutocomplete();
}
// Alternatively you can do
var autocomplete = accEl.attributes.get("autocomplete");
if (["list", "both"].indexOf(autocomplete) != -1) {
doAutocomplete();
}
Attribute list
Set of exposed attributes depends on semantics of the element. As an example, typical attributes are:
DOMString autocomplete;
- Exposed on text fields. Values are list, none, inline, both.
DOMString live;
- Points that the accessible is live region. Values are assertive and polite.
DOMString relevant;
- Lists all notifications that qualifies for live region.
Patterns
A pattern is a collection of attributes or methods that expresses an accessible element semantics and compliments what the AccessibleElement interface provides. The patterns concept is quite similar to attributes but tends to be more powerful. Basically, it is an alternative implementation of COM's queryInterface.
AccessibleElement .patterns
- Returns a list of all patterns supported by the accessible element.
Object .toPattern(DOMString type)
- Returns an object for the pattern of given type if supported by an accessible element.
See patterns section for details.
Relations
AccessibleElement? .relativeOf(DOMString type)
- Returns related accessible element of the given relation type. If relation points to multiple accessible elements, the first one is returned.
RelationMap .relations
- Returns a map of relation types as keys and related accessible elements as values.
interface RelationMap {
maplike<DOMString, sequence<AccessibleElement>>;
};
Relation types
This is a typical list of relation types that may be exposed by an accessible element. Note, the accessible element may support custom relations as well.
labelfor
- Referred accessible element is an element that is labelled by this accessible element.
labelledby
- Referred accessible element is a label for this accessible element.
descriptionfor
- Referred accessible element is an element that is described by this accessible element.
describedby
- Referred accessible element is a description for this accessible element.
widget
- Return a widget the item belongs to.
parent
- Return a logical parent of the item. This relation may be useful for ARIA structures if the browser doesn't convert DOM flat structure into accessible hierarchical tree.
Examples
Console logging of all headers of the grid cell and name of the grid itself.
var headers = cell.relations.get("labelledby");
for (let header of headers) {
console.log(header.role, header.name);
}
var grid = cell.relativeOf("widget");
console.log(grid.name);
Actions
An accessible element may support actions that can be invoked on it. For example, jump on a link or press on a button, or it can be generic purpose actions like scroll or focus. Certain accessible actions may take optional parameters.
AccessibleElement .actions
- Returns a ActionMap object of actions exposed by the accessible element. The returned object is not live, i.e. it is not updated if the accessible element actions change.
AccessibleElement .activate(in DOMString name, in optional any param)
- Invokes the accessible action.
- Parameters:
- name
- action name to invoke
- param
- used to provide extra context for the action
Performs the given accessible action on the accessible element.
Action list
activate
- Exposed on accessible elements that may be activated. Accessible elements may use other names for this action to emphasize the semantics they expose. For example, jump on links, press on buttons, check and uncheck on checkboxes. Accessible element may provide more than one action. For example, tree item can provide select/unselect as its primary action and expand/collapse as secondary. Tree column may implement sort action.
focus
- Focus on an accessible element. May be different from "activate" action, for example, in case of buttons where "activate" means press.
scroll
- Scrolls an accessible element into view, optionally takes coordinates relative the element to scroll the view to
- Parameter:
- delta of ScrollDelta
drag and drop
- Used to start dragging and dropping the content related to the accessible element the action is invoked on.
zoomin / zoomout
- Zooms in/out the content corresponding the accessible the action is invoked on.
- Parameter:
- ratio of double, optional
undo / redo
- Performs clipboard operations on the accessible element of the editable content.
ScrollDelta param
directory ScrollDelta {
int x;
int y;
int z;
DOMString mode;
};
ScrollDelta structure describes a scroll change within the accessible element, the scroll change can be expressed in different units, for example, it can be in pixels or in pages. The accessible element may provide its custom set of supported modes which has to be described in taxonomy.
ScrollDelta .x, .y, .z
- 3d coordinates in the units provided by mode, y and z might be optional depending on the unit.
ScrollDelta .mode
- A unit the coordinates are measured in. Can be on of the following values:
- pixel - x, y and z (optional) specifies how many pixles to scroll (2d or 3d)
- line - x specifies how many lines to scroll
- paragraph - x specifies how many paragraphs to scroll
- page - x specifies how many pages to scroll
ActionMap
Accessible actions are presented by ActionMap map like object of pairs { action name, action object }.
interface ActionMap {
readonly maplike<DOMString, Action>;
};
Each action is presented by Action interface.
interface Action {
stingifier readonly attribute name;
readonly attribute description;
readonly InteractionSet interactions(optional DOMString device);
};
Action .name
- Action name
Action .description
- Localized action description
Action .interactions
- Set of interactions (like keyboard shortcuts or mouse gestures) to invoke the action.
- Parameters
- device (optional)
- device name like 'keyboard' or 'touchscreen' the interactions should be returned for.
Here's an example of script announcing available actions on the accessible element.
var set = accElm.actions;
if (set.size() == 0) {
say("no actions on accessible element");
} else {
say("accessible element has " + set.size() + " actions");
set.forEach(action => say(action.description));
}
Interactions
A widget may support actions that can be invoked through variety of devices or by AT like screen readers. The way the action is triggered by the user is described by the interaction. Examples of user interactions are swipe, a mouse gesture to toggle a switch control; space, a key to toggle a checkbox. Access keys (alt+letter) and keyboard shortcuts (ctrl+shift+letter) used to activate the widgets are also examples of interactions. Complex widgets like grid control may support several actions, for example ctrl+A for selectall action, ArrowDown/ArrowUp keys for movedown/moveup actions, ArrowRight/ArrowLeft keys for movenext/moveprev actions.
The AT may need to know the used shortcuts to avoid possible conflicts or to supply a native way to invoke the action. For example, if presentation supports swipe gesture to navigate the slides then the AT can announce this info for the user.
AccessibleElement .interactions
- Return an InteractionSet object describing all interactions that can be performed with the accessible element.
interface InteractionSet {
readonly maplike<DOMString, Interaction>;
boolean hasAnyOf(sequence<DOMString> interactions);
readonly attribute InteractionSet allOf(DOMString action, optional DOMString device);
};
AccessibleElement .hasAnyOf
- Return true if any of given interaction are in use by the widget.
- Parameters:
- interaction
- list of interactions
AccessibleElement .allOf
- Return a list of all interactions with the accessible element as InteractionSet used to invoke the given action on the given device.
- Parameters:
- action
- action name
- device
- a device name, examples of supported values are "keyboard", "mouse", "touchpad".
interface Interaction {
stingifier readonly attribute description;
readonly attribute device;
};
Here's an example of the screen reader announcing all interactions of swipe action.
var actions = accElm.actions;
actions.forEach(action => { var set = action.interactions;
say(action.name);
set.values().forEach(item => say(item.description));
});
Questions/concerns
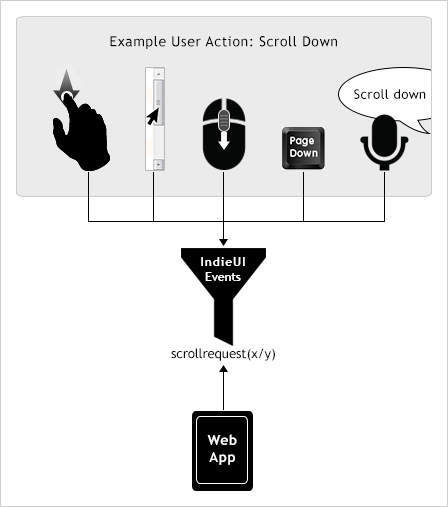
- Interactions should be extended to allow to specify a control that triggers the action. The concept is described by InidieUI: you can use mouse, touchscreen, keyboard, voice control or a control element to invoke the action. Maybe Interactions should be renamed to Triggers to share terms with IndieUI.
Here's the image of InideUI action/interaction concept.
Alternatively we could introduce relations between actions like "triggers" and "triggeredby".
- What about highlevel actions (uberactions), for example, "press" buttons means "send something somewhere". This may be covered by label. Another example, selected listitem on the left changes a view on the right, "select" actions has meaning of "change view". Or checkbox that enables/disables related controls, "check/uncheck" action means "enable/disable controls". These examples correlates to controlledby/controllerfor relations, but the relations doesn't reveal type of control.
Parent-child relations
The interface provides a bunch of methods to provide access to parent/child relations between accessible elements.
AccessibleElement .parent
- Returns the parent accessible element if any.
AccessibleElement .firstChild
- Returns the first child accessible element if any.
AccessibleElement .lastChild
- Returns the last child accessible element if any.
AccessibleElement .nextSibling
- Returns the next sibling accessible element if any.
AccessibleElement .previousSibling
- Returns the previous sibling accessible element if any.
AccessibleElement .children
- Return AccessibleChildren collection of all child accessible elements.
interface AccessibleChildren {
iterable<AccessibleElement>;
};
Questions/concerns:
- Consider to move "widget" relation to "widget" IDL attribute (property) under this section.
Accessible providers
The accessible element can be created with different kinds of sources. Most of the accessible elements are created for a DOM element to expose its semantics to the assistive technology. In some cases the browser may not have underlying DOM node for the content. In this case the accessible object is created, without having a corresponding DOM element. In some cases a web author may need to change the semantics for existing elements, add new semantics or create a new accessible subtree to make content accessible. In this case the author needs to describe desired semantics in JavaScript. See Making the content accessible in JavaScript for details.
AccessibleElement .DOMNode
- Returns a DOM node associated with the accessible element if any. Accessible element does not have a DOM node when it is either not based on it, or when it has been detached from the DOM node. The first case happens for browser-specific implementations or for trees created in JavaScript. The second case happens when the JavaScript holds reference to the object longer than the object life cycle.
AccessibleElement .source
- Returns AccessibleSource if present, refers to an accessible source, used to override accessible properties of the element.
Content traversal
This section describes how to traverse accessible content, for example, if you need to navigate a document by headings or navigate a paragraph by words.
A key concept of the content traversal is accessible position which describes a "location" in the document content. A position can be placed on an accessible element, for example, on a button. It can be placed before or after an accessible element, or inside of the accessible element text, for example, at the end of the first line of a paragraph.
The position can be moved forward or backward inside the document to the content complying with the given criteria. For example, criteria can be described verbally like "move the position forward to next heading" or "move the position one word back".
Accessible Position
[Constructor(AccessibleElement anchor, optional Offset offset, optional AccessibleElement root),
Constructor(DOMNode container, long offset, optional AccessibleElement root),
Constructor(DOMPoint point, optional AccessibleElement root),
Constructor(AccessiblePos pos, optional AccessibleElement root)]
interface AccessiblePos {
AccessiblePos? move(AccessibleElement anchor, Offset offset);
AccessiblePos? move(DOMNode container, long offset);
AccessiblePos? move(DOMPoint);
AccessiblePos? move(Where where, Criteria);
AccessiblePos? search(Where where, Criteria);
readonly attribute AccessibleElement root;
readonly attribute AccessibleElement? anchor;
readonly attribute Offset offset;
DOMRangeBound toDOM();
};
typedef AccessiblePos A11ePos; // Short and nice name? // Maybe accPos
Construction
Construction by accessible element and offset relative it.
AccessiblePos .Constructor(AccessibleElement, Offset, AccessibleElement)
- Constructs the accessible position.
- Parameters
- elm of AccessibleElement
- anchor accessible element of the position
- offset of Offset, optional
- an offset relative to the anchor element. If not provided then at or afterbegin is used depending on element type.
- root of AccessibleElement, optional
- a root of subtree containing the position. If not provided then parent document is used.
The offset may be either a number, a numeric mapping of caret position in the content, or a literal.
typedef long or OffsetLiterals Offset;
enum OffsetLiterals {
"before",
"begin",
"at",
"end",
"after"
};
OffsetLiterals .before
- Used to set the accessible position right before the accessible element beginning.
OffsetLiterals .begin
- Used to set the accessible position right after the accessible element beginning.
OffsetLiterals .at
- Used to set the accessible position at the accessible element.
OffsetLiterals .end
- Used to set the accessible position right before the accessible element ending.
OffsetLiterals .after
- Used to set the accessible position right after the accessible element ending.
Example #1. Input widget.
<input id="input" value="Hello">
<script>
var input = document.getElementById("input").a11ement;
// Position is at the control
var p = new A11ePos(input, "at");
// Position is in the control text at 0 offset.
p = new A11ePos(input, "begin");
// Position is in the control text at 5 offset.
p = new A11ePos(input, "end");
</script>
Example #2. Image inside a paragraph.
<p id="p">I <img id="img" src="love.png" alt="love"> you</p>
<script>
var img = document.getElementById("img").a11ement;
// The position is right before the image, at 2 offset relative the paragraph.
var p = new A11ePos(img, "before");
// The position is right after the image, at 3 offset relative the paragraph.
p = new A11ePos(img, "after");
// The position is at the image, no offset relative the paragraph is applicable.
p = new A11ePos(img, "at");
p = new A11ePos(img, "begin");
p = new A11ePos(img, "end");
</script>
Example #3. Table.
<table id="table">
<tr>
<td>cell</td>
</tr>
</table>
<script>
var table = document.getElementById("table").a11ement;
// The position at the table.
var p = new A11ePos(table, "at");
// The position is in the table, before the row.
var p = new A11ePos(table, "begin");
// The position is in the table, after the row.
var p = new A11ePos(table, "end");
// The position is in the table, before the row, numeric offset is ignored.
var p = new A11ePos(table, 1);
</script>
Construction from a point on the screen. See hit testing for details.
AccessiblePos .Constructor(DOMPoint, AccessibleElement)
- Constructs the accessible position.
- Parameters
- point of DOMPoint
- a point, the accessible position should be set at
- root of AccessibleElement, optional
- a root of subtree containing the position. If not provided then parent document is used.
Construction from a DOM node and offset relative it. See selection section for examples.
AccessiblePos .Constructor(DOMNode, long, AccessibleElement)
- Constructs the accessible position from (DOMNode, offset) pair.
- Parameters
- node of DOMNode
- the container node
- offset of long
- offset within the container node
- root of AccessibleElement, optional
- a root of subtree containing the position. If not provided then parent document is used.
Copy constructor.
AccessiblePos .Constructor
- Constructs the accessible position equal to given position.
- Parameters
- pos of AccessiblePos
- accessible position to copy
Change the position
There is a bunch of methods to change accessible position.
AccessiblePos .move(AccessilbeElement, Offset)
- Move the accessible position to the given anchor and offset.
- Parameters
- element of AccessibleElement
- the anchor
- offset of Offsest, optional
- offset relative the anchor
- Return itself or null if not succeeded.
AccessiblePos .move(DOMNode, long)
- Move the accessible position to the given DOM node at given offset.
- Parameters
- node of DOMNode
- the anchor
- offset of long
- offset relative the anchor
- Return itself or null if not succeeded.
AccessiblePos .move(DOMPoint)
- Move the accessible position in the content. Returns true if succeeded.
- Parameters
- point of DOMPoint
- the point the accessible position should be moved to.
- Return itself or null if not succeeded.
Move through the content
Accessible position can be moved through the content by criteria.
AccessiblePos .move (Where, Criteria)
- Move the accessible position to the content complying with criteria.
- Parameters
- where of Where
- where the search should be performed
- criteria of Criteria
- function describing a match
- Return itself if succeeded, otherwise null.
AccessiblePos .search (Where, Criteria)
- Search for content of the given criteria relative the accessible position.
- Parameters
- where of Where
- where the search should be performed
- criteria of Criteria
- function describing a match
- Return new instance if succeeded, otherwise null.
Where to search
The search area and the way accessible elements are traversed are defined by Where argument. It defines whether traversal is perfromed by accessible tree hierarchy or by layout on the screen, and whether the traversal is relative of the current position or relative of the root.
enum Where {
"forward",
"backward",
"cyclic forward",
"cyclic backward",
"tofirst",
"tolast",
"left",
"right",
"up",
"down",
"above",
"under",
"closest"
};
Where .forward
- Search after the accessible position.
Where .backward
- Search backwards from the accessible position.
Where .cyclic forward
- Search forwards from the accessible position in cycle.
Where .cyclic backward
- Search backwards from the accessible position in cycle.
Where .first
- Search for a first match inside the root.
Where .last
- Search backwards (from last to first element) for a first match inside the root.
Where .left
- Search for a match left to the position.
Where .right
- Search for a match right to the position.
Where .up
- Search for a match up from the position.
Where .down
- Search for a match down from the position.
Where .above
- Search for a match above the position.
Where .under
- Search for a match under the position.
Where .closest
- Search for a geometrically closest match to the position.
Example.
function criteria(el) { }
var pos1 = new A11ePos(new DOMPoint(x, y), a11edoc).move("forward", criteria);
var pos2 = new A11ePos(elm, "at").move("backward", criteria);
var pos3 = new A11ePos(pos).move("forward", criteria);
or
var pos2 = pos2.search("forward", criteria);
Criteria
Criteria can be either a literal describing how the position should be moved or a matching function called for every traversed accessible.
typedef CriteriaLiteral or CriteriaFunc Criteria;
enum CriteriaLiteral {
"char",
"word",
"sentence",
"line",
"paragraph",
"change",
"bit"
};
CriteriaLiteral .char
- Used to move the position one char long.
CriteriaLiteral .word
- Used to move the position to the next word.
CriteriaLiteral .sentence
- Used to move the position to the next sentence.
CriteriaLiteral .line
- Used to move the position to beginning of next line or end of previous line.
CriteriaLiteral .paragraph
- Used to move the position to beginning of next/previous paragraph.
CriteriaLiteral .change
- Used to move the position to next change either of text attribute or new accessible.
CriteriaLiteral .bit
- Used to move the position to next/previous navigable position. For example, from accessible start inside of it to right before accessible outside of it or moving from end of this line to start of next line in case of soft line break lines.
Example #1. Traverse a paragraph by words.
var p = document.getElementById("p").a11ement;
var pos1 = new A11ePos(p, "begin", p), pos2 = null;
while (pos2 = pos1.search("forward", "word")) {
console.log(pos2.text(pos1));
pos1 = pos2;
}
<p id="p">Mozilla is a <a href="">free-software</a> community which produces the <a href="">Firefox web browser</a>.</p>
The script above generates the log "Mozilla ", "is ", "a ", "free-", "software ", "community", "which ", "produces ", "the ", "Firefox ", "web ", "browser."
<p id="p">Mo<a href="">zilla</a>.</p>
The log is "Mozilla".
callback CriteriaFunc = CriteriaLiteral or Offset or "next" (AccessibleElement);
CriteriaFunc
- A criteria function used to define an algorithm of the match.
- Returns
- a criteria term or offset(s)
If "next" is returned then criteria function is reentered with next traversed accessible. If offset is given then traversing is stopped, the accessible position is moved to the traversed accessible element and given offset. If criteria literal is returned then the accessible position is moved to the position complying the criteria. If it cannot be moved withing current accessible then it reenters with next accessible.
Example. Navigate by widgets and structures, and by words in case of text.
function criteria(aEl)
{
var role = document.taxonOf("role", aEl.role);
if (role.is("widget")
return "at";
if (role.is("structure")
return "at";
// Reenters with next accessible if it cannot move to the next line within this accessible.
if (role.is("textcontainer"))
return "line";
return "next";
}
pos.move("next", criteria);
Other methods
AccessiblePos .root
- Returns the accessible element the position movement is restricted to.
AccessiblePos .anchor
- Returns the accessible element the position is at or contained by.
AccessiblePos .offset
- Return an offset of the accessible position, either numeric or text.
AccessiblePos .toDOM
- Returns DOMRangeBound object which is a pair of DOM node and content offset relative it.
dictionary DOMRangeBound {
DOMNode node;
long offset;
};
Virtual cursor
Virtual cursor is accessible position attached to the accessible document. It's unique per document.
partial interface AccessibleDocument {
AccesiblePos cursor;
};
Whenever the virtual cursor position is changed then cursor_moved event is fired.
Questions/concerns
- Do we need *is* method right on AccessibleElement or should we have Role interface having that method or should AccessibleElement return role taxa as a role.
- Do we need to have "inContextOf" on AccessibleElement to check what the accessilbe belongs to. Note, native implementation doing some cache may be faster than tree traversal. If we need it then it's worth to consider *is* method too.
- Do we need isAnyOf() method additionally?
- Do we need to compare() method to compare two positions
- Ensure that the virtual cursor is survivable. If it ends up in the hidden sub-tree for example. If subtee gets destroyed then cursor should be moved. If AccessiblePos doesn't have matching function then it's unclear where it should be moved.
- Also take into account walking to/from parent/child frames
- Should it be outlined as moved?
- Yura: we should have async API for search.
[ Promise variant if we had async API].
function getText() {
var p = new A11ePos().move("first", a => a.role == "paragraph");
var startPos;
return p.then(function(pos) {
startPos = pos;
return pos.search("forward", a => "line"); }).
then(function(endPos) {
return startPos.textInBetween(endPos);
};
}
getText().then(function(text) { /* Say text */ })
Text
partial interface AccessiblePos {
DOMString text(AccessiblePos pos);
DOMString text(CriteriaLiteral criteria);
readonly attribute AttributeSet textAttributes;
};
AccessibleDocument .text(AccessiblePos)
- Returns the text enclosed between this and given accessible positions.
AccessibleDocument .text(CriteriaLiteral)
- Returns the text at the position complying the given criteria. See criteria for options.
Example how to get first line of the first encountered paragraph:
function criteria(a)
{ return a.role == "paragraph" ? "being" : "next" };
var startPos = new A11ePos(document).move("first", criteria);
var endPos = startPos && startPos.search("forward", "line");
var text = startPos.text(startPos, endPos);
or same effect by using criteria literal
function criteria(a)
{ return a.role == "paragraph" ? "being" : "next" };
var pos = new A11ePos(document).move("first", criteria);
var text = pos.text("line");
Text attributes
AccessibleDocument .textAttributes
- Returns a AttributeSet of all text attributes presented at this accessible position.
List of text attributes [to complete]
color
- Text color
background-color
- Background color of text
Example
<p id="p">hello <b>bold</b></p>
var pos = new A11ePos(document.getElementById("p").a11ement, 7);
p.textAttributes.get("font-weight") == 700; // true
Caret and selection
Document accessible provides bunch of methods to operate on text selection and caret.
partial interface AccessibleDocument {
attribute AccessiblePos caret;
attribute AccessiblePos? selectionStart;
attribute AccessiblePos? selectionEnd;
};
AccessibleDocument .caret
- Returns accessible position for the caret.
AccessibleDocument .selectionStart
- Get/set selection start.
AccessibleDocument .selectionEnd
- Get/set selection end.
Example.
var pos = new A11ePos(new DOMPoint(event.x, event.y)); document.a11ement.selectionStart = pos; var pos2 = new A11ePos(pos.anchor.nextSibling); document.a11ement.selectionEnd = pos;
Example #2. Connection with DOM selection.
var sel = window.getSelection(); var pos1 = new A11ePos(sel.anchorNode, sel.anchorOffset); var pos2 = new A11ePos(sel.focusNode, sel.focusOffset); var p1 = pos1.toDOM(); sel.getRangeAt(0).setStart(p1.node, p1.offset); var p2 = pos2.toDOM(); sel.getRangeAt(0).setEnd(p2.node, p2.offset);
Geometry
The section contains bunch of methods and approaches to deal with web page geometry.
Outline
AT can outline a position or a range enclosed between two positions. This feature is useful to track stuff like virtual cursor.
partial interface AccessibleDocument {
void outline(AccessiblePos pos1, optional AccessiblePos pos2);
void clearOutlines();
};
AccessibleDocument .outline
- Outlines a position if second position is omitted. If second position is omitted then outlines a collapsed range.
AccessibleDocument .clearOutlines
- Removes all drawn outlines.
AT can scan the web page by moving the position geometrically up/down/left/right.
var scanner
{
start: function() {
if (this.stopped)
return;
var nextpos = this.pos.move("right", this.controller);
if (!nextpos)
nextpos = this.pos.move("down", this.controller);
if (nextpos) {
document.outline(nextpos);
window.setTimeout(this.start.bing(this), 1000);
}
},
stop: function() {
this.stopped = true;
},
controller: function(aEl) {
var role = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", aElm.role);
if (role.is("widget"))
return "at";
return "next";
}
pos: new A11ePos(new DOMPoint(0, 0)),
stopped: false
}
Hit testing
The author can do accessible position to match the accessible element of given criteria at given position.
<script>
function onmove(aEvent)
{
// Announce name of the accessible element pointed by mouse.
var atcursor = new A11ePos(new DOMPoint(event.x, event.y));
say(atcursor.anchor.name);
// Locate a nearest control.
var atwidget = atcursor.search("closest", a => document.taxonOf("role", a.role).is("widget"));
if (atwidget)
say(atwidget.name);
};
</script>
<body onmove="onmove(event);></body>
Questions/concerns
- Outline: it's tricky to style that but maybe document or accessible should decide how it should be styled, for example, black outline on black background.
- Do we need a way to return coordinates of accessible position's edge points?
- Do we need a method to calculate distance between two positions?
- Do we need a method to calculate boundaries (aka containing rect)?
- Do we need a method to check whether the given point is contained by a range?
Events
The accessible element may fire various number of events. You can add event listener on document accessible to handle all events from accessible elements belonging to the document.
callback AccessibleEventListener (AccessibleEvent event);
partial interface AccessibleDocument {
void on(DOMString eventType, AccessibleEventListener listener);
void off(DOMString eventType, AccessibleEventListener listener);
};
AccessibleDocument .on
- Adds event listener of the given event type.
AccessibleDocument .off
- Removes event listener of the given event type.
All event objects implement AccessibleEvent interface.
interface AccessibleEvent {
readonly attribute DOMString type;
readonly attribute AccessibleElement target;
readonly attribute AttributeMap attributes;
};
AccessibleEvent .type
- Event type.
AccessibleEvent .target
- Event type accessible element target.
AccessibleEvent .attributes
- Extra attributes used to describe the event. Used for certain event types.
Example. Live regions processing.
function handleLiveRegion(aEvent)
{
var attrs =
{ live: "assertive", relevant: "change:name" };
if (aEvent.attributes.hasAllOf(attrs)) {
say(aEvent.target.name);
}
}
document.a11ement.on("change:name");
Event types
[section needs to be completed]
"focus"
- Fired when accessible element is focused.
"caretmove"
- Fired when caret is moved within the document.
"change:name"
- Fired when name property is changed.
Patterns
Controls may expose own patterns to expose their semantics if it cannot be expressed by accessible element properties.
Value controls
Control elements having numeric value like slider, progressbar, meter or numberbox implement AccessibleValue inteface.
interface AccessibleValue {
readonly attribute long max;
readonly attribute long min;
readonly attribute long low;
readonly attribute long high;
readonly attribute long optimum;
readonly attribute long step;
readonly attribute long value;
};
Group info
Item elements provides information about their group and their position in the group.
interface AccessibleGroupInfo {
readonly attribute long count;
readonly attribute long index;
readonly attribute long level;
};
Tables
A cell of tables and grids provide the interface for 2 dimensional navigation. Cell headers can be obtained by labelledby relation.
interface AccessibleTableCell {
readonly attribute unsigned long rowIndex;
readonly attribute unsigned long colIndex;
readonly attribute unsigned long rowSpan;
readonly attribute unsigned long colSpan;
};
AccessibleTableCell .rowIndex
- Return row index of the cell.
AccessibleTableCell .colIndex
- Return column index of the cell.
AccessibleTableCell .rowSpan
- Return number of rows that the cell is spanned to.
AccessibleTableCell .colSpan
- Return number of columns that the cell is spanned to.
Multiprocessing
Accessible tree is scoped to a process, i.e. you can have seamless accessible tree between all document frames until it violates security policy. In case of multiprcess frames you have to use standard mechanism to communicate between processes.
When the virtual cursor reaches a frame start or end and it was attempted to move it further then message is sent to a process where the virtual cursor would go in case of single process.
Questions/concerns
- what messaging mechanism should be used
- should it be allowed to move from iframe to parent document?
Make the content accessible
You can tweak the accessible tree right in JS. You can do both:
- extend the native semantics of the DOM element by overriding its accessible properties,
- create whole accessible trees for inaccessible content, for example, for graphics, charts in a canvas.
Direct change of accessible properties
Accessible element properties can be altered right on the accessible element. Changing accessible property will result in accessible events if needed. For example:
<button id="button"></button>
<script>
var div = document.getElementById("button").a11ement;
div.name = "click me";
div.description = "test accessibility";
</script>
Accessible name and description are changed for the accessible button, "name changed" and "description changed" events are fired. Note, it changes neither visual appearance of the button nor DOM button element properties. If affects on accessible element of the button only.
States
parital interface StateSet {
void set(DOMString ... states);
void unset(DOMString ... states);
void toggle(DOMString state);
};
StateSet .set
- Set given states on the accessible element.
StateSet .unset
- Unset given states from the accessible element.
StateSet .toggle
- Toggle the state on the accessible element.
Example.
<div role="checkbox" onclick="disableEnable();">
<div role="listbox" id="listbox"/>
<script>
function disableEnable()
{
var listbox = document.getElementById("listbox").a11ement;
listbox.states.toggle("disabled");
}
</script>
Attributes
You can add/change/delete attributes on the accessible element. For example,
var listbox = document.getElementById("listbox").a11ement;
listbox.attributes.set("autocomplete", "list");
Relations
partial interface RelationMap {
void add(DOMString relation, AccessibleElement element);
void remove(DOMString relation, AccessibleElement element);
};
RelationMap .add
- Puts the accessible element into relations.
RelationMap .remove
- Breaks the given relations between these accessible elements.
var label = document.getElementById("label");
var control = document.getElementById("control").a11ement;
control.relations.add("labelledby", label.a11yment);
Extend the semantic via accessible source
Alternatively you can extend native semantic of a DOM element by connecting it to an accessible source, the object describing accessible element. If the DOM node is not accessible then setting the accessible source on it makes it accessible. Otherwise the given source lands on top of the existing accessible object.
partial interface Node {
attribute AccessibleSource? accessibleSource;
};
If the DOM node is accessible then you can provide accessible source by setting it up right in AccessibleElement.
partial interface AccessibleElement {
attribute AccessibleSource? source;
};
The source object used to describe the accessible element implements AccessibleSource interface which basically portrays properties of AccessibleElement interface.
callback interface AccessibleSource {
readonly attribute DOMString role;
readonly attribute sequence<DOMString> states;
readonly attribute DOMString name;
readonly attribute DOMString description;
readonly attribute DOMString value;
readonly attribute object attributes;
readonly attribute object relations;
readonly attribute sequence<DOMString> patterns;
object toPattern(DOMString);
readonly attribute DOMString text;
object textAttributesAt(Offset);
readonly attribute object actions;
void activate(DOMString action);
AccessibleElement? element;
};
Basics
AccessibleSource .role
AccessibleSource .states
AccessibleSource .name
AccessibleSource .description
AccessibleSource .value
- These properties corresponds to properties of AccessibleElement interface.
Example #1. Override accessible name of the button.
If the author needs to change accessible name of the HTML button
<button id="btn">press me</button>
then he can do this either with ARIA
document.getElementById("btn").setAttribute("aria-label", "new name");
or set it directly on the accessible element
document.getElementById("btn").a11ement.name = "new name";
or by setting its accessible source
document.getElementById("btn").accessibleSource = { name: "new name"; }
These are two equivalent approaches that can be used same time and mixed with each other the way that better fits the author's intent. It's important to keep in mind though that the accessible source has a priority over ARIA attributes. Setting up the accessible source doesn't operate on DOM and thus it's supposed to be more performant as extra layer is excluded between the author and accessibility engine. Another benefit of setting the accessible source is improved code readability since the author is able to point multiple properties at once in declarative way. For example,
<script>
document.getElementById("btn").accessibleSource = {
name: "new name",
description: "new description",
states: [ "disabled" ]
};
</script>
Attributes and relations
AccessibleSource .attributes
- A map of attribute names and their values applied to the accessible element
AccessibleSource .relations
- A map of relation types and relations for this accessible element. The bunch of types may be used to point out related elements. You can use either Node, AccessibleElement or AccessibleSource objects. In latter case the object has to be in the accessible tree, in other words, it has to have associated accessible element when relation is poked by AT.
Example #2. Adding semantics.
The accessible source can be also used when the author wants to add semantics to semantically neutral element. For example, the author can turn an ordinal HTML div element into listbox control:
<label id="label">Names:</label>
<div id="list"></div>
<script>
var listboxSource = {
role: "listbox",
relations: {
"labelledby": [ document.getElementById("label") ]
}
};
var listboxNode = document.getElementById("list");
listboxNode.accessibleSource = listboxSource;
</script>
It's worth to notice that accessible source approach like ARIA doesn't require the author to provide comprehensive description, i.e. correlating properties may be skipped. For example, presented labelledby relation makes unnecessary to provide accessible name. The browser should handle this on its own.
Example #3. Lazy computations.
The previous example may look bulkier than its ARIA equivalent:
var listboxNode = document.getElementById("list");
listboxNode.setAttribute("role", "listbox");
listboxNode.setAttribute("aria-labelledby", "label");
but its benefit is it allows accessible properties lazy computation. An accessible property whose value isn't changed during whole life cycle of its accessible element or which doesn't require an accessible event on its change is good candidate for lazy computation. For example the previous example may be modified this way:
var listboxSource = {
role: "listbox",
relations: {
get labelledby() {
return document.querySelectorAll("*[listboxlabel]");
}
}
};
In this case the labelledby relation getter is more powerful than its ARIA version and all computations are running iff somebody inquired the relation.
Patterns
AccessibleSource .patterns
- Returns a list of all patterns implemented by the accessible element.
AccessibleSource .toPattern
- Returns an object for the given pattern. If the method is not provided then the source object has to implemented itself all claimed patterns.
Example #4. Implement patterns.
var slider = {
role: "slider",
patterns: [ "value" ],
toPattern: function(aName) {
return aName == "value" ? this : null;
},
min: 0,
max: 100,
value: 0
};
Text
AccessibleSource .text
- Return the text.
AccessibleSource .textAttributesAt
- Returns object of { name: value } pairs representing text attributes at given offset within the accessible element text.
Example #5. Text content.
While text should be normally in the content, there are cases when the author has to provide it for non-text content. For example, this technique can be used to turn HTML image into text.
<div id="container"></div>
<script>
var elm = document.getElementById("container");
elm.innerHTML = "I " + <img src="love.png"> + "you";
var psource = {
role: "paragraph",
text: "I love you",
textAttributesAt: function(aOffset) {
if (aOffset >= 5 && aOffset <= 7) {
return { color: "red" }; // "love" is red
}
}
};
elm.accessibleSource = psource;
</script>
Actions
AccessibleSource .actions
- Return all supported actions on the accessible element.
AccessibleSource .activate
- Invoke the given action.
- Parameters
- action
- the action name to invoke
Example #6. Describe actions and interactions.
function listitem(aName)
{
return {
role: "treeitem",
name: aName,
actions: {
select: {
interactions: [ { mouse: "click" } ]
}
}
};
};
In case if interactions cannot be provided then the accessible source have to implement activate method to invoke actions.
Inheritance
AccessibleSource .element
- Refers to the accessible element implementation as there were no accessible source attached to it. Set by the browser when the accessible source is attached to the accessible element.
Example. Lazy extension of accessible relations.
var source = {
get relations() {
var r = this.element.relations;
r.add("labelledby", document.querySelector(this.selector));
return r;
},
element: null,
selector: ""
};
document.getElementById("button").accessibleSource = source;
Change the accessible tree
The web developer can alter existing accessible tree including subtree creations and deletions. This can be done either by AccessibleSource object assigned to the accessible element or by direct manipulations on the accessible tree.
Direct tree alteration
Accessible source object can be used to create new accessible element and insert it into the tree. If DOM node is used as a source then associated subtrees of accessible elements within the DOM node are reparanted, i.e. they are removed from children of its current accessible parent and added as children of new parent. Accessible element can be removed from children.
partial interface AccessibleChildren {
void append(AccessibleSource or DOMNode ... children);
void insertBefore(AccessibleElement before, AccessibleSource or DOMNode ... children);
void insertAfter(AccessibleElement after, AccessibleSource or DOMNode ... children);
void replace(AccessibleSource or DOMNode ... children);
void remove(AccessibleElement ... children);
void clear();
};
Children .append
- Appends accessible elements provided by sources as children to the accessible element.
Children .insertBefore
- Inserts accessible elements provided by sources before the given child.
Children .insertAfter
- Inserts accessible elements provided by sources after the given child.
Children .replace
- Replaces existing children accessible elements within elements provided by sources.
Children .remove
- Removes accessible elements from the accessible tree.
Children .clear
- Removes all child accessible elements.
Example
<input id="input" role="combobox">
<div id="list" role="listbox">
<div role="listitem">choice1</div>
<div role="listitem">choice1</div>
</div>
<script>
var input = document.getElementById("input").a11ement;
input.children.replace(document.getElementById("list"));
</script>
Build up the tree via accessible source
You can provide child accessible elements for the given accessible element by assigning AccessibleSource object to it. This approach allows to create whole portions of the accessible tree for the content having no underlying DOM nodes.
partial interface AccessibleSource {
sequence<AccessibleSource or DOMNode> children;
};
AccessibleSource .children
- Return collection of accessible children. If AccessibleSource is provided then it's used to create a new accessible element and insert it as a child. If accessible DOMNode is provided then its accessible element is used, if inaccessible DOMNode is provided then its accessible children if any are used.
Example. Add list with items into the tree.
var tree = {
role: "listbox",
name: "colors",
children: [
{
role: "listitem",
states: "focusable",
name: "red"
},
{
role: "listitem",
states: "focusable",
name: "green"
}
]
};
divNode.accessibleSource = tree;
Canvas hit regions
Canvas hit region options are extended by a11ement which is used to connect accessible element with hit region. Whenever hit region is activated then activate method of connected AccessibleSource object is called with no argument provided.
Say you have a canvas with drawn button. In order to make it accessible you can create accessible button right in JS.
var source = {
role: "button",
name: "test",
actions: {
click: {
interactions: {
mouse: "click"
}
}
},
onactivated: function(aEvent) {
if (aEvent.region == "button")
this.element.set("focused");
else
this.element.states.unset("focused");
}
element: null // set by the browser
};
canvasNode.addHitRegion({ id: "button", a11ement: source });
canvasNode.addEventListener("click", source.onactivated.bind(source));
Feedback notifications
Accessible element may be notified of any kind of event, including about property change when managed by connected source object. When notified the browser may fire accessible events and update its cache if necessary. Decision whether to notify the browser or not should be based on the accessible events model. In other words if a property change in native markup causes accessible event then it's quite likely the event is expected for similar accessible source change.
partial interface AccessibleElement {
void notifyOf(DOMString eventType, optional Object attrs);
};
AccessibleElement .notifyOf
- Called when source has been changed to notify the host accessible element about property change. The browser is responsible to fire proper accessible events and update its internal representation.
- Parameters
- eventType of DOMString
- The event type to fire.
- attrs
- Attributes describing the event. See event types for attributes variety.
If the above listbox gets disabled then you have to reflect that in its state:
var listboxSource = {
role: "listbox",
name: "breed list",
states: "disabled",
get element() { return this.elm; }
set element(aElm) {
this.elm = aElm;
this.elm.notifyOf("change:name");
this.elm.notifyOf("change:states", { added: "disabled" });
}
};
function onfocus(aEvent) {
// Change accessible properties when element is focused.
// The change requires accessible events.
aEvent.target.accessibleSource = listboxSource;
}
Implied semantics
The idea is to help the author to keep the code less verbose as possible. If role implies a number of preset attributes or states then they are present on the accessible element by default, i.e. if the author didn't list them. For example, if listitem role is selectable and focusable by default then the author doesn't have to point selectable and focusable states when he describes a listitem source, in other words, these code snippets are equivalent:
var source1 = {
role: "listitem"
};
var source2 = {
role: "listitem",
states: [ "selectable", "focusable" ]
};
Implied semantics is described by taxonomies.
Conflicts
[to be done conflicts between native semantics, ARIA and this API, I tend to think that the author should be able to replace/remove native semantics if needed. This can ruin the web page but it gives the absolute control over the page content. A dangerous but quite powerful tool like atomic energy. ]
Sniffing
In order to make an optimization, the content provider has to know whether an accessibility consumer (like screen reader) is active. The provider can add a callback for deploy and conceal event types which will be triggered when consumer appears/gets inactive.
function deployA11y() {
// build accessible tree or update existing one
// keep the tree updated
}
function stopA11y() {
// stop keeping the accessible tree updated
}
document.a11ement.on("deploy", deployA11y);
document.a11ement.on("conceal", stopA11y);
Semantics providers
The author of the content which is not a standard HTML has to provide content semantics to make the content accessible. In other words, he has to describe a semantic vocabulary that will be used to give the content specific meaning. For example, if you are ebook publisher then you will need a bunch of new roles like 'bibliography' or 'appendix'. If you do operate with complex widgets then likely you will need to describe its states, attributes or relations.
partial interface AccessibleDocument {
void import(DOMString name, Object taxonomy);
};
AccessibleDocument .import
- Import the taxonomy.
- Parameters
- name of DOMString
- taxonomy name like role or states
- taxonomy of Object
- a collection of taxa and their properties.
- Throws
- if there's names conflict or there are invalid relations between taxonomies then an exception should be thrown [todo].
Depending on taxonomy type, a taxa may be described by specific fields and be connected with other taxonomies. For example, DPUB semantics may be described this way:
document.accessibleElement.import("role",
{
appendix: {
parents: "section",
landmark: "appendix",
description: "appendix"
},
bibliography: {
parents: "list",
landmark: "bibliography",
owns: "biblioentry",
description: "bibliography"
},
biblioentry: {
parents: "listitem",
description: "reference"
}
}
This approach is alternative to DPUB ARIA extensions. Any web app operating with DPUB content can import JS file describing the taxonomies and the browser can expose the content properly to the assistive technology. No special support on the browser side is required.
In short reasons to provide taxonomy are:
- The browser automatically maps the content to desktop accessibility APIs;
- The web accessibility technology knows how to expose the content;
- Adds implied accessibility support for the content;
- Automatic content validation.
Taxonomies
You can get hierarchical relations between roles, states, actions or anything else that has a taxonomy. For example, if the web author introduces a role 'checklistitem' which is compound from two roles 'checkbox' and 'listitem', i.e it inherits properties of both of them then the web author should integrate the new role into existing role hierarchy. Taxonomies are scoped by AccessibleDocument which provides bunch of methods to get them.
partial interface AccessibleDocument {
Taxon? taxonOf(in DOMString taxonomy, in DOMString name);
Taxonomy? taxonomyOf(DOMString name);
};
AccessibleDocument .taxonOf
- Returns a taxon for the given taxon name of requested taxonomy.
- Parameters
- taxonomy
- a taxonomy name
- name
- name of requested taxa like 'button' in case of 'role' taxonomy
AccessibleDocument .taxonomyOf
- Return an object describing requested taxonomy.
- Parameters
- name
- a taxonomy name
interface Taxon {
stringifier readonly attribute DOMString name;
readonly attribute DOMString description;
readonly attribute sequence<Taxon> parentTaxa;
readonly attribute sequence<Taxon> childTaxa;
bool is(DOMString or Taxon base);
readonly attribute AttributeMap attributes;
readonly attribute RelationMap relations;
};
Taxon .name
- Return name of the taxa
Taxon .description
- Return localized description of the taxa
Taxon .parentTaxa
- Return list of taxa the taxon is inherited from.
Taxon .childTaxa
- Return list of taxa that is inherited from this taxon.
Taxon .is
- Return true if given taxon name is in base of the taxon.
Taxon .attributes
- Return a map between attribute names and attribute values specific for the taxon.
Taxon .relations
- Return a map between relation types and related taxa specific for the taxon.
Example #1. Handle new role as it was known.
var taxa = {
checklistitem: {
parents: [ "checkbox", "menuitem" ]
}
};
document.a11ement.import("role", taxa);
var taxon = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", "checklistitem");
if (taxon.is("menuitem")) {
// process menuitem selection
}
Example #2. Checking whether role is a navigational landmark.
var taxon = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", "main");
var isLandmark = taxon.attributes.has("landmark");
Example #3. Getting states specific to the role.
var taxon = document.a11ement.taxonOf("role", "listbox");
print(listboxRole.relations.get("states"))); // prints "focusable"
Managing the taxonomies
interface Taxonomy {
Taxon? taxonOf(DOMString name);
readonly attribute sequence<Taxon> rootTaxa;
void addTaxon(DOMString name, sequence<Taxon or DOMString> baseTaxa);
void removeTaxon(Taxon taxon);
};
Taxonomy .getTaxon
- Return a taxon object for the given name.
- Parameters
- name
- taxon name
Taxonomy .rootTaxa
- Return list of base taxa
Taxonomy .addTaxon
- Adds new taxon into the taxonomy.
- Parameters
- name
- a new taxon name
- baseTaxa
- a list of taxa the taxon is inherited from
Taxonomy .removeTaxon
- Remove the given taxon and all taxa inherited from it from the taxonomy.
- Parameters
- taxon
- taxon object
Taxonomy types
Each taxonomy is described means of its own interface which is used to define the hierarchy and interconnections between taxonomies. If taxon refers to taxa of other taxonomy type then a string describing the reference may be in form of "taxon:modifier", where taxon is a name of related taxon and modifier is an extra information about how the taxa are interconnected. For example, role taxon may be connected to "live" taxon of attributes taxonomy by placing "live:assertive" value in attributes field which means that the role supports "live" object attribute and its default value is "assertive" on it.
Roles
dictionary RoleTaxon {
DOMString landmark;
DOMString description;
sequence<DOMString> parents;
sequence<DOMString> owns;
sequence<DOMString> states;
Object attributes;
sequence<DOMString> relations;
sequence<DOMString> actions;
};
RoleTaxon .landmark
- Navigation landmark name if applicable.
RoleTaxon .description
- Localized role description.
RoleTaxon .parents
- List of roles the role is inherited from.
RoleTaxon .owns
- List of roles allowed in children of the role. Used for validation.
RoleTaxon .states
- List of states allowed on the role. Optional modifier is "default" which points out that the state is exposed on the role until explicitly specified otherwise. See implied semantics.
RoleTaxon .attributes
- List of attributes supported by the role. Default value of the attribute may be specified as modifier. For example, "live:polite" points out that "live" object attribute has "polite" value by default. If default value is not specified then it's taken from referred attribute taxon description.
RoleTaxon .relations
- List of relations supported by the role.
RoleTaxon ..actions
- List of supported actions. Actions from the list are exposed on the accessible element depending on states present on it. For example, if supported actions are "check" and "uncheck", then "check" is exposed if the accessible element doesn't have "checked" state, otherwise "unchecked".
Example. ARIA textbox role.
var taxa = {
widget: { }
input: {
parents: [ "widget" ],
states: [ "focusable:default", "focused" ]
},
textbox: {
description: "text field",
parents: [ "input" ],
states: [
"singleline:default", "multiline",
"editable", "readonly",
"required"
],
attributes: [ "autocomplete" ]
}
};
Example. ARIA checkbox role.
var taxa = {
checkbox: {
description: "checkbox",
parents: [ "input" ],
states: [ "checkable:default, "checked" ],
actions: [ "check", "uncheck" ]
}
};
Example. ARIA log role.
var taxa = {
region: {
},
log: {
parents: [ "region" ],
attributes: [ "live:polite" ]
}
};
States
dictionary StateTaxon {
DOMString description;
sequence<DOMString> dependents;
DOMString exclusives;
}
StateTaxon .description
- Localized taxa description.
StateTaxon .dependents
- List of all dependent states. For example, "focused" state always accompanied by "focusable" state.
StateTaxon ..exclusives
- Mutually exclusive states if applicable. For example, if "vertical" state is applied then "horizontal" is not and vice versa.
Example.
var taxa = {
focusable: {
dependents: [ "focused" ]
},
focused: { },
singleline: {
exlcusives: [ "multiline" ]
},
multiline: {
exlcusives: [ "singleline" ]
},
readonly: { },
editable: { },
required: { },
checked: {
exlusives: [ "mixed" ]
},
mixed: {
exlusives: [ "checked" ]
}
};
Attributes
interface AttributeTaxon {
DOMString description;
sequence<DOMString> values;
DOMString default;
};
AttributeTaxon .description
- Localized description of the taxon
AttributeTaxon .values
- List of all possible values of the attrbiute
AttributeTaxon .default
- Default attribute value. Takes a place if role taxa pointing to it doesn't have own default value of it.
Example
var taxa = {
autocomplete: {
values: [ "none", "list", "inline", "both" ],
default: "none"
},
live: {
values: [ "none", "polite", "assertive" ],
default: "none"
}
};
Actions
dictionary ActionTaxon {
DOMString description;
DOMString dual;
sequence<DOMString> states;
};
ActionTaxon .description
- Localized action description.
ActionTaxon .dual
- Dual action taxon. When action is invoked, it is switched to its dual action if applicable.
ActionTaxon .states
- Implied states. When action is invoked, states of dual action are cleared, this action states are set.
Example.
var taxa = {
check: {
description: "check",
dual: "uncheck",
states: [ "checked" ]
},
uncheck: {
description: "uncheck",
dual: "check"
}
};
HTML and beyond
This doc introduces common patterns to express the semantics of markup languages to accessibility. Markup specifics is not a target for this doc in general. Each markup specification has to take care to describe their accessibility stuff in terms of this API.
Extensibility
The web application might need to extend default taxonomies to express the new semantics. For example, the web service publishing music sheets can introduce new characteristics like role, states, etc to describe music sheet content. However the web application should take care to explain new characteristic by extending default taxonomies, i.e. by describing the connection between old and new characteristics. That will resolve any backward compatibility issue, so if the consumer doesn't know about new roles then he can still figure out a closest match it's aware about. For example, if the web app author introduces "x-redbutton' and provides a role taxonomy for it saying this is an extension of 'button' role, then the consumer unfamiliar with 'x-redbutton' role will treat it as a button.
The author should follow name convention to avoid potential collisions with future additions into the spec predefined lists. Thus all names should be prefixed by 'x-' like 'x-redbutton' from example above.
Music sheet example
To make a music sheet accessible the web app may introduce bunch of new roles, attributes and relations:
roles: 'sheet' - inherited from 'section' 'note' - inherited from 'image', describes the note
role 'sheet' attributes: instrument: DOMString, tempo: number/DOMString clef: DOMString
role 'note' attributes:
key: enum { C, D, E, F, G, A, H },
alteration: enum { none, flat, sharp },
octave: enum { ... },
duration: number,
effects: sequence<DOMString>, // tremolo, bend
role 'note' relations: crescendo: [note, ...] a list a notes the crescendo is applied to diminuendo: [note, ...] a list a notes the diminuendo is applied to
Or in terms of taxonomies:
document.import("role", {
sheet: {
description: "sheet",
attributes: [ "instrument", "tempo", "clef" ]
},
note: {
description: "note",
attributes: [ "key", "alteration", "octave", "duration", "effects" ],
relations: [ "crescendo", "diminuendo" ]
}
});
document.import("attributes", {
instrument: {
description: "instrument type"
},
tempo: {
description: "tempo"
},
clef: {
description: "clef"
},
key: {
description: "key",
values: [ "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "A", "H" ],
},
alteration: {
description: "alteration",
values: [ "none", "flat", "sharp" ],
default: "none"
},
octave: {
description: "octave",
values: [ "contra", "great", "small", "1line", "2line" ],
},
duration: {
description: "duration"
},
effects: {
description: "effects"
}
});
document.import("relations", {
crescendo: {
description: "crescendo"
},
diminuendo: {
description: "diminuendo"
}
});