PluginUpdating: Difference between revisions
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
This page will do a check on common plug-ins and see if they are vulnerable or not. [http://www.guninski.com/mozbugs/plug-test.html An example implementation can be found here.] | This page will do a check on common plug-ins and see if they are vulnerable or not. [http://www.guninski.com/mozbugs/plug-test.html An example implementation can be found here.] | ||
Plug-ins to check: | |||
* Java (system update) | * [http://java.com/en/download/installed.jsp?detect=jre&try=1 Java] (system update) | ||
* Flash (provides API, system update) | * [http://www.adobe.com/shockwave/welcome/ Flash] (provides API, system update) | ||
* Windows media player ( | |||
Future plug-ins to check: | |||
* Windows media player (system update) | |||
* Real player (system update) | |||
* Quicktime (system update) | * Quicktime (system update) | ||
== Mock-up == | == Mock-up == | ||
| Line 53: | Line 56: | ||
== Determining the latest secure version == | == Determining the latest secure version == | ||
Ideally we would talk to the upstream provider and get the latest secure version. However, initially we can just maintain a file that includes the latest versions of the plug-ins. | Ideally we would talk to the upstream provider and get the latest secure version. However, initially we can just maintain a file that includes the latest versions of the plug-ins. | ||
== We found an insecure plug-in, now what? == | |||
After we detect that a plug-in is out of date, we should open the vendor page in a new tab. | |||
One major concern is that each plug-in update needs a browser restart. | |||
=== Java === | |||
[http://java.com/en/download/installed.jsp?detect=jre&try=1 Sun provides an update check]. Linking here should provide a sufficient starting point for getting java up to date. | |||
=== Flash === | |||
[http://www.adobe.com/shockwave/welcome/ Adobe provides an update check]. The user will be offered to navigate to this page for the update. | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
Revision as of 18:18, 6 August 2007
Problem Statement
Our users often get hacked via vulnerable third party plug-ins.
Proposal
Add scripts on common landing pages to check for vulnerable plug-ins and assist the user in updating them.
Components
- Script and alert on landing pages
- Page that checks all the common plug-ins and assists in the update
Landing pages
First Run
Add an alert that checks the first time a user opens Firefox:
Message: We detected that some of your media plug-ins are vulnerable, click here for more info.
This is non-evasive, as we do not want to have the user have trouble getting started with Firefox.
stick mock-up and plans for how it will look here
This will lead the user to the plug-in check page.
Updated
Add similar alert to the "you've been updated" page which leads to the plug-in check page.
Implementation
It will be easiest to check the basic functionality in Javascript. Bug 282258 has some script for checking if Java is up to date.
UpYourPlug page
This page will do a check on common plug-ins and see if they are vulnerable or not. An example implementation can be found here.
Plug-ins to check:
Future plug-ins to check:
- Windows media player (system update)
- Real player (system update)
- Quicktime (system update)
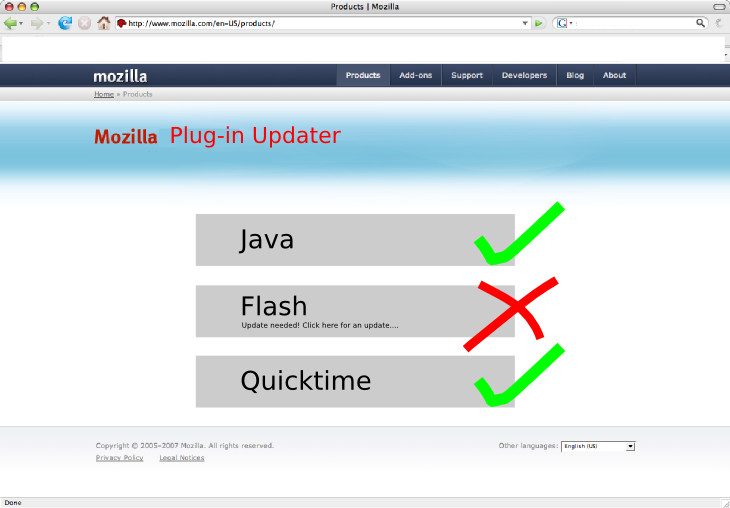
Mock-up
Here is a cheesy mock-up of the idea for the plug-in update check page.
Implementation
Some of the plug-ins, such as Flash, provide an API for checking for security updates. Therefore, the check could easily be implemented in the language of the plug-in if it provides such API. Otherwise, it will need to be done in JavaScript.
Some pseudo code:
if plug-in flash is installed display flash based flash security update check if plug-in java is installed run javascript based java security update check ...
Determining the latest secure version
Ideally we would talk to the upstream provider and get the latest secure version. However, initially we can just maintain a file that includes the latest versions of the plug-ins.
We found an insecure plug-in, now what?
After we detect that a plug-in is out of date, we should open the vendor page in a new tab.
One major concern is that each plug-in update needs a browser restart.
Java
Sun provides an update check. Linking here should provide a sufficient starting point for getting java up to date.
Flash
Adobe provides an update check. The user will be offered to navigate to this page for the update.