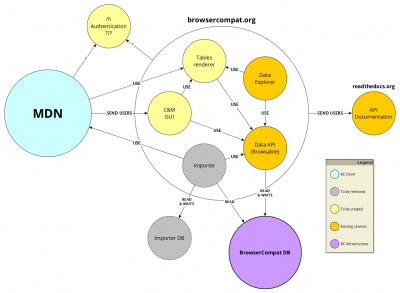
MDN/Development/CompatibilityTables/Infrastructure
Here's a schema for the browsercompat.org services:
The BrowserCompat (bc) components are:
- MDN - primary consumer of compatibility data
- Data API - primary data data source
- BrowserCompat DB - stores current compatibility data
- Data Explorer - to browse compatibility data
- Importer - Scrapes data from MDN and injects into Data API
- Importer DB - stores extra import data
- C&M GUI - Contribution and moderation interface
- Table renderer - for MDN and other services
- Authentication - end-user authentication services
- API documentation - describes data schema, other parts
Development
A local development copy of MDN is not required for BC development. MDN is backed by the mozilla/kuma project. Development is done using a local VM that provides many of the production services. See the installation documentation for details.
The Data API is in the mdn/browsercompat project. It is a Django project. Developers will need to install a Python development environment, and optionally will need PostgreSQL, Memcached, and Redis installed. See the Installation documentation for details.
The BrowserCompat DB can be a PostgreSQL database (recommended) or a SQLite database. It requires the Data API to setup the schema and populate the data. Compatibility data is periodically exported to the mdn/browsercompat-data project, and can be used to populate a developer's database.
The Data Explorer is part of the mdn/browsercompat project code base, and requires a local install of the Data API for development.
The Importer is part of the mdn/browsercompat project code base, and requires a local install of the Data API for development.
The Importer DB is currently part of the BrowserCompat DB. Local development may require a lengthy scraping of the MDN site.
The C&M interface is backed by the mdn/browsercompat-cm project. It is running Ember.js, with the ember-cli project. Developers will need to install the dependencies, including Node.js, Bower, ember-cli, and PhantomJS. See the README.md for details.
The Table Renderer is still in planning, and the project has not started. A prototype renderer is implemented in KumaScript, in the EmbedCompatTable macro.
Local accounts are used for Authentication. For development, it is easiest to create local Django accounts backed by username and password. ./manage.py createsuperuser can be used to create a superuser account with access to the Django admin.
The API documentation is hosted at browsercompat.readthedoc.org, and sourced in the mdn/browsercompat project. Documentation developers will need to install the Data API to build documents locally, but won't need to populate it with compatibility data.
Current Testing and Deployment Process
MDN is a mature product, with many layers of testing:
- Developers can run unit tests against their own code (
./manage.py test) - Pull Requests are tested in TravisCI
- Each pull request is reviewed by another developer using GitHub's PR interface.
- When accepted, PRs are merged to the master branch.
- The master branch is periodically deployed by a developer to staging at https://developer.allizom.org. Deployment is controlled by a script in the repository, and usually does not include manual steps.
- Developers and staff perform targeted manual testing of new features on staging.
- Intern is used to run client-side tests against the staging server.
- When testing is complete, the code is deployed to production. Developers monitor the site for 1 hour after production pushes, to be aware of any performance degradation.
A single codebase is used for the Data API, Data Explorer, Importer, and API Documentation. This project includes testing:
- Developers can run
make testto run Django unit tests, andmake qato run code linters and coverage tests as well. - Developers can run
make test-integrationto run a local API instance, load it with sample data, and make API requests. - Pull requests are tested in TravisCI. This runs unit, QA, and integration tests.
- Some pull requests are code reviewed by other developers, because 1) the API does not include personally identifiable information, 2) the service is not in production use outside of some beta testers, and 3) no other developers are currently familiar with the code.
- When ready, PRs are merged to the master branch
- When the master branch is updated, the documentation is rebuilt and deployed to https://browsercompat.readthedocs.org
- The master branch is tested in TravisCI again.
- When testing is successful, the code is automatically deployed to https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com
Heroku hosts the BrowserCompat DB and the Importer DB in a single RDS PostgreSQL database. When the data schema changes, database migrations are run using the command-line heroku client (heroku run --app browsercompat ./manage.py migrate)
The C&M GUI is in early development. Developers can run tests with ember test, but 100% success is not yet expected. No tests are automatically run on push.
Authentication is done against https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com, and is not specifically tested. Firefox Accounts was integrated, but has since broken.
The KumaScript-based table renderer is manually tested, and requires manually refreshing MDN pages when data changes. Stephanie Hobson has a test page linking to interesting pages.
Current Infrastructure
MDN has a mature infrastructure, maintained in a data center. It include load balancers, databases, search servers, admin nodes, and worker nodes. It also has a parallel staging infrastructure. The interface between MDN and the BrowserCompat services is over HTTP, so the MDN infrastructure does not matter to the BrowserCompat services, or vice-versa.
Many components run in Heroku at https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com:
- Data API: https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com/api/v2
- Data Explorer: https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com/browse/
- Importer: https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com/importer/
- Authentication: https://browsercompat.herokuapp.com/accounts/login/
The websites run on a Hobby Dyno, and async tasks run on a second Hobby Dyno. Add-ons are used for Memcache and Redis services, and a PostgreSQL add-on hosts both the BrowserCompat DB and the Importer DB.
The C&M GUI is currently not deployed.
The Tables renderer doesn't exist yet.
API Documentation is hosted at http://browsercompat.readthedocs.org/en/latest/
On The Way To Production
To do
Production Services
Note: this is the proposed infrastructure, and hasn't been reviewed by operations or QA
MDN is planning to move to an AWS-based infrastructure in Q1/Q2 2016.
MDN will add an OAuth2 provider interface, to allow BrowserCompat users to use their MDN account on BrowserCompat sites.
BrowserCompat will be deployed as a set of small services hosted on subdomains of browsercompat.org:
- https://browsercompat.org will redirect to https://www.browsercompat.org
- https://www.browsercompat.org - the Data Explorer and C&M GUI' server / load balancer
- https://api.browsercompat.org - the Data API server / load balancer
- https://importer.browsercompat.org - the Importer server, retired after import is complete.
- https://integrate.browsercompat.org - the Table Renderer server / load balancer
- https://www.cdn.browsercompat.org - assets for the C&M GUI interface
- https://api.cdn.browsercompat.org - assets for the Data API server
- https://admin.browsercompat.org - deployment coordinator
- https://qa.browsercompat.org - Jenkins server for testing and deployment
Backend services will not be publicly available, but will use a similar DNS scheme:
- db01.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - BrowserCompat DB and Importer DB (primary)
- db02.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - BrowserCompat DB and Importer DB (replica)
- www01.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the C&M GUI
- www02.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the C&M GUI
- api01.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the Data API
- api02.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the Data API
- api03.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the Data API
- worker01.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Async task worker supporting the Data API
- worker02.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Async task worker supporting the Data API
- cache01.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Caching server (Redis)
- cache02.prod.internal01.browsercompat.org - Caching server (Redis)
- broker01.prod.internal01.browsercompat.prg - Messaging broker (Redis)
"*.internal01.browsercompat.org" identifies servers in a particular datacenter. This may be replaced with another name that matches the actual datacenter ("ec2-usw2.browsercompat.org"), or are picked by the deployment backend (Heroku, [Deis http://deis.io]).
A parallel infrastructure will be used for staging:
- https://www.stage.browsercompat.org - the Data Explorer and C&M GUI server / load balancer
- https://api.stage.browsercompat.org - the Data API server / load balancer
- https://importer.stage.browsercompat.org - the Importer server, retired after import is complete.
- https://integrate.stage.browsercompat.org - the Table Renderer server / load balancer
- https://www.stage.cdn.browsercompat.org - assets for the C&M GUI interface
- https://api.stage.cdn.browsercompat.org - assets for the Data API server
Staging will have parallel backend servers, but without the same redundancy:
- db01.stage.internal01.browsercompat.org - BrowserCompat DB and Importer DB
- www01.stage.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the C&M interface
- api01.stage.internal01.browsercompat.org - Web worker supporting the Data API
- worker01.stage.internal01.browsercompat.org - Async task worker supporting the Data API
- redis01.stage.internal01.browsercompat.org - Caching server and messaging broker (Redis)
When needed, some or all of a load testing infrastructure will be deployed:
- https://www.load.browsercompat.org - the Data Explorer and C&M GUI server / load balancer
- https://api.load.browsercompat.org - the Data API server / load balancer
- https://importer.load.browsercompat.org - the Importer server, retired after import is complete.
- https://integrate.load.browsercompat.org - the Table Renderer server / load balancer
- https://www.load.cdn.browsercompat.org - assets for the C&M GUI interface
- https://api.load.cdn.browsercompat.org - assets for the Data API server
as well as backends appropriate for the load test, and as many load testing servers as needed.